Radiology of urinary system
Dr. Sameer Abdul Lateef* Infestation by Schist. Haematobium.
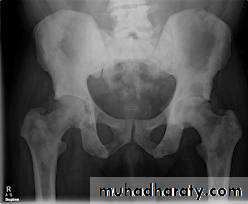
*The ova deposited into sub-mucosa of urinary bladder and to less extent at the wall of ureters .*The ova calcify and excrete toxin producing necrosis of tissue lead to granulomatous tubercles and extensive fibrosis .
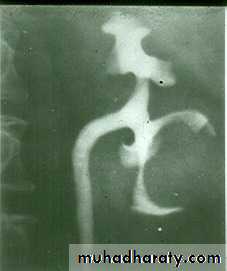
*Calcification is very common and important diagnostic findings. Very common in bladder ,less frequent in lower ureters ,but in advanced case involve the whole length of ureter .
*The appearance depends on degree of fullness of bladder ; thin linear opacity outlining bladder wall.
Empty bladder shows crowded linear opacities with calcified plaques.
Urinary Schistomiasis
• IVU: Early stage –cobble stone Later filling defects due to graneulomatos papilloma Carcinoma is important complication Ureters : dilated and tortuousIn early stage hydroureter and hydronephrosis + refluxSPACE OCCUPING LESION
SIMPLE RENAL CYST* Common cause of renal mass .
* Uncommon under age of 30 years , most common over 50 years .
* Single or multiple .
* Usually cortical in origin .
* Varies in size ; few mm to 25 cm .
* Contains straw color fluid , with thin fibrous wall lines by flat epithelium .
* Clinically silent , large cyst can shows palpable mass .
* Calcification is rare , normal renal function .
Renal cyst cont.
KUB :1- Cyst in upper pole displace kidney downward . Cyst at medial surface displace the kidney laterally .with enlarged kidney
2- Smooth local bulge of renal out-line.
3- Calcifications rare 3% usually in hemorrhagic cyst.
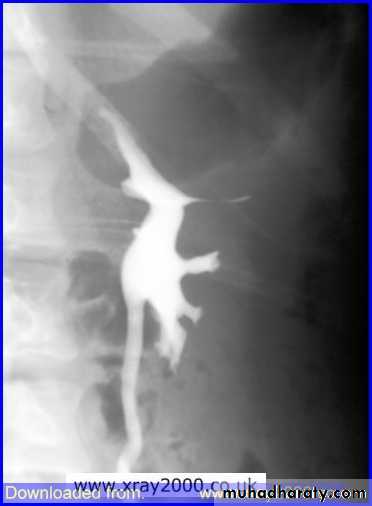
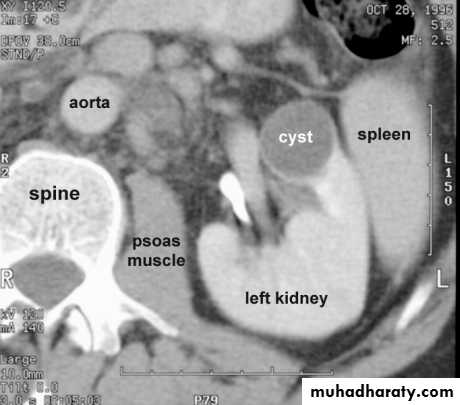
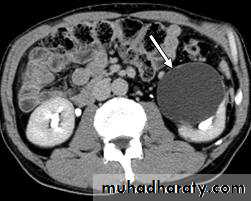
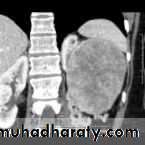
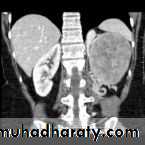
Renal S.O.L (cyst)
RENAL CYST
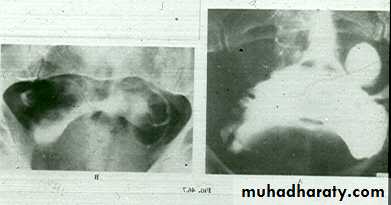
IVU :-* Nephrogram shows filling defect .
*Displacement , elongation & stretching of PCS which depend on size and site of the cyst .
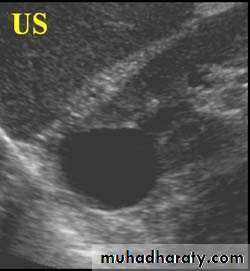
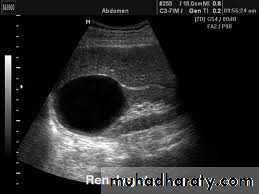
US :-
shows echo-free cystic lesion with posterior enhancement.
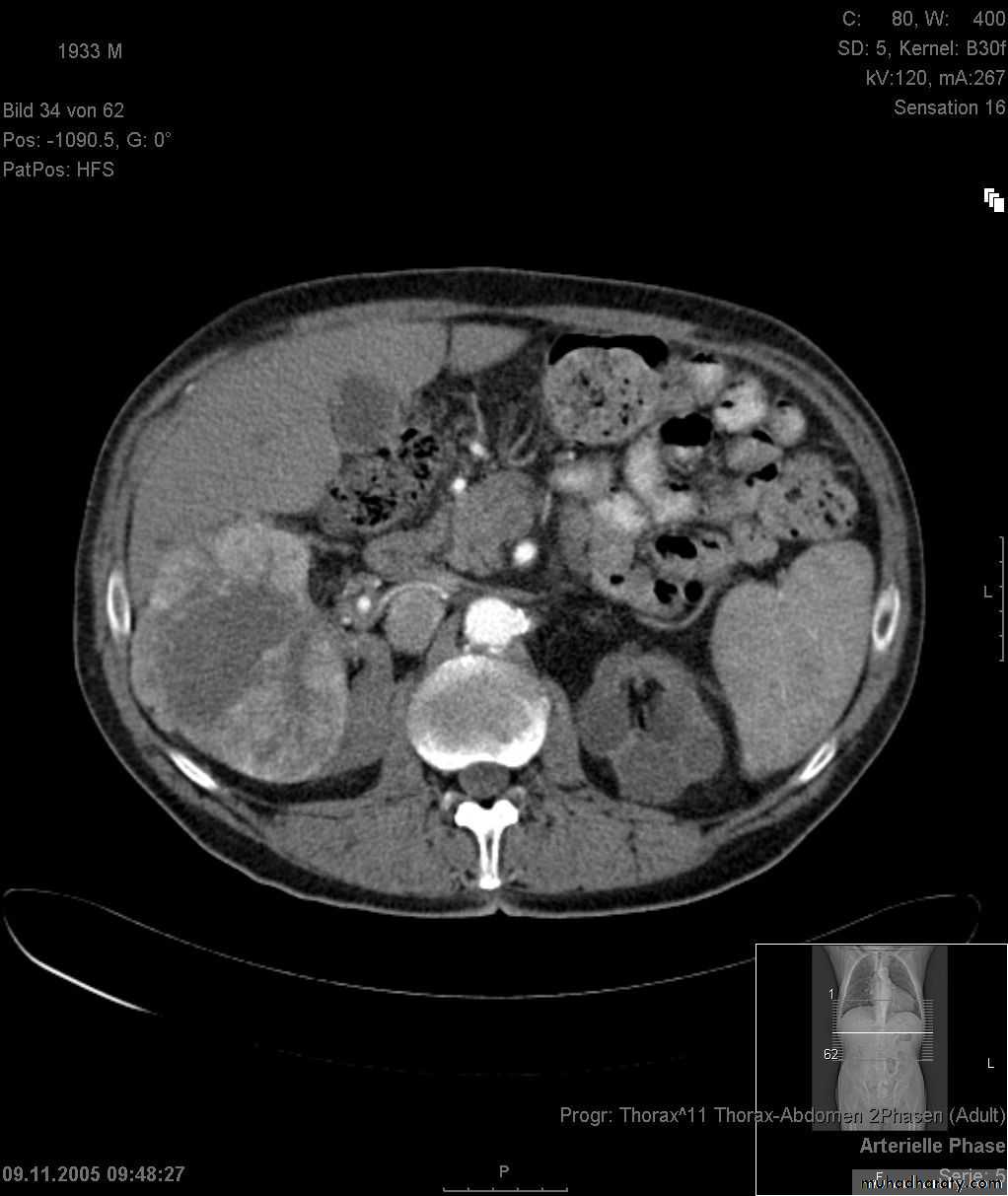
RENAL TUMOR Adenocarcinoma ( Hyper nephroma)
* Comprise 80% of renal malignant tumor. next epithelial T. of renal pelvis (transitional cell Ca.) ; Nephroblastoma ( Wilm’s Tumor ).* Clinically may be silent or presented with loin pain , heamaturia and loin mass .
* Usually unilateral , rare bilateral .
KUB :-
* Soft tissue mass.
* Bulging in renal out-line .
* Diffuse renal enlargement .
* Calcification occur in 6 % of cases .
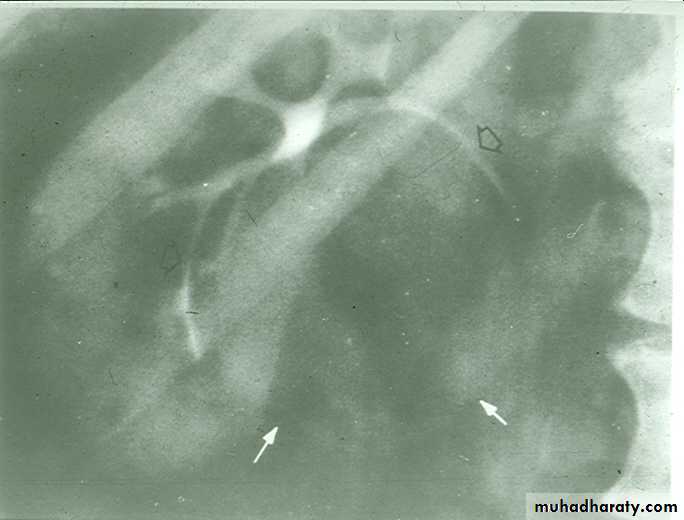
IVU :-
* Nephrogram shows filling defect which is irregular .* Distracted PCS .
* Hydronephrosis.
* Amputation & missing calyces .
* Large non-functioning kidney .
Angiogram
US
CT
MRI
WILM’S Tumor
Most common abdominal malignancy in childhood( 1 – 5 years ) , 3% bilateral
KUB & IVU:-
Large soft tissue mass displacing bowel loops , distracted calyces ,Non functioning kidney
Epithelial tumor of renal pelvis
BLADDER Tumor
* Common tumor of urinary tract .* The are of epithelial origin and all are malignant.
Radiological appearance :-
Filling defect in cystogram stage , well defined or lobulated , plaque like and irregular in non-papillary type .
Calcification in plain film due to encrusting of urinary salts.
Ureteric obstruction
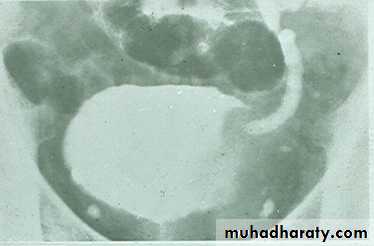
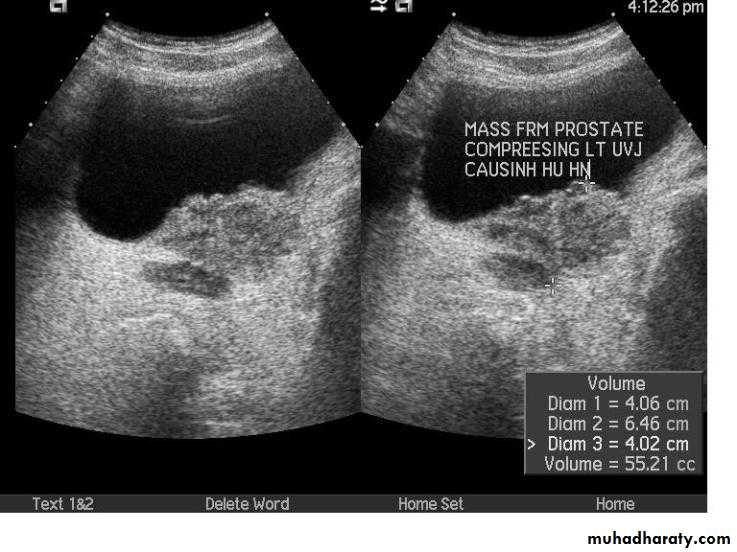
PROSTATIC Enlargement
Common cause of lower urinary obstruction . Either Benign prostatic hyperplasia or Carcinoma .Benign Hyperplasia :-
Plain film:-
* Enlargement of bladder shadow due to residual urine.
*Prostatic calculi or calcification .
• IVU ( cystogram stage )
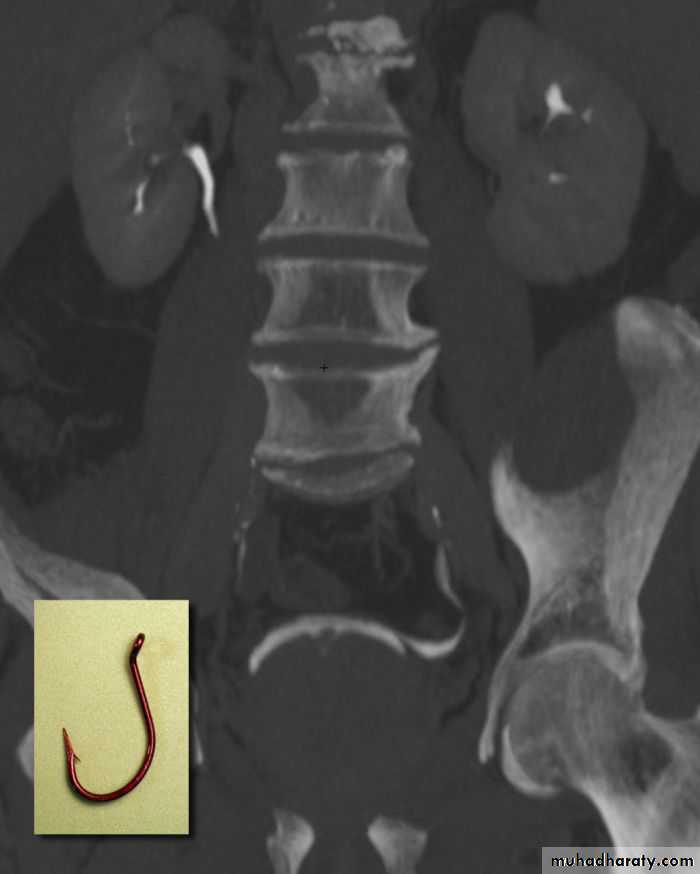
• * Elevated bladder base .• *Lower ureter elevated and curved (fish hook ).
• * Back pressure to both kidney & ureters .
• * Thick trabeculated bladder wall and diverticula formation .
• * Large size prostate produce filling defect like appearance .
• * Post-voiding residual volume .
•
Produce similar changes except:
* Plain film shows evidence of metastasis to the bone especially in the pelvis .* The prostatic urethra shows irregular narrowing and stretching .
* US can distinguish between BPH & Ca.