Classification of Head Injuries
Scalp InjuriesSkull Injuries
Intra-cranial Injuries (Brain Injuries)
C. Intracranial Injuries (Brain Injuries)
Types of Brain InjuriesI. Primary Brain Injury: at the time of the impact (e.g. contusions and lacerations) and is irreversible.
II. Secondary Brain Injury:occurs at some time after the moment of impact and is often preventable.
The management of head injury is aimed at preventing secondary injury.
The causes of secondary brain injuries
Hypoxia.Hypotension: systolic blood pressure (SBP) <90 mmHg
Raised intracranial pressure (ICP): ICP>20 mmHg
Low cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP): CPP<65 mmHg
Pyrexia
Seizures
Metabolic disturbances
I. Primary Brain Injury
• Diffuse Axonal Injury.
• Cerebral Concussion.
• Brainstem and hemispheric (Cerebral ) Contusion.
• Cortical Lacerations.
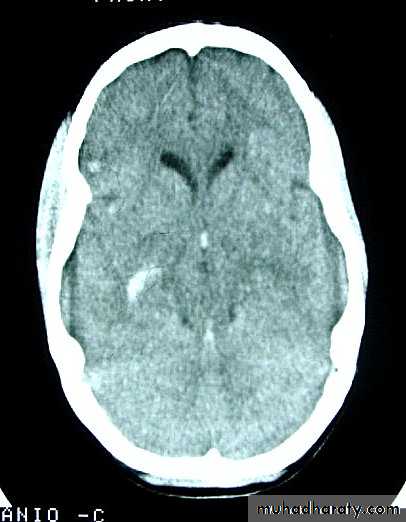
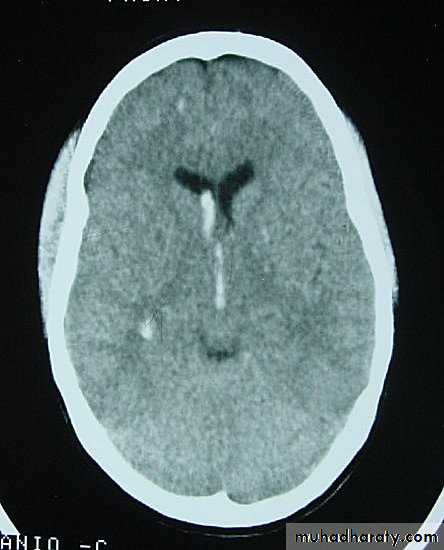
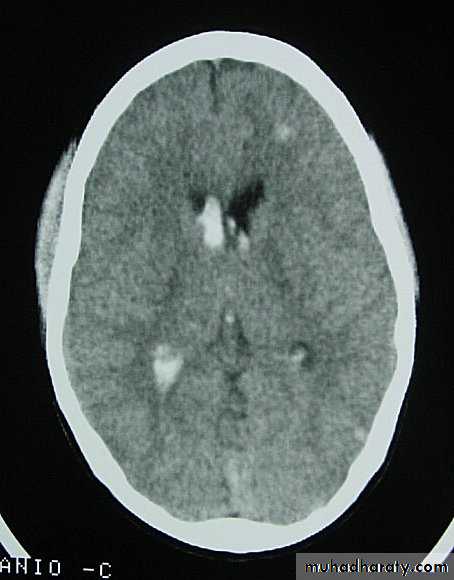
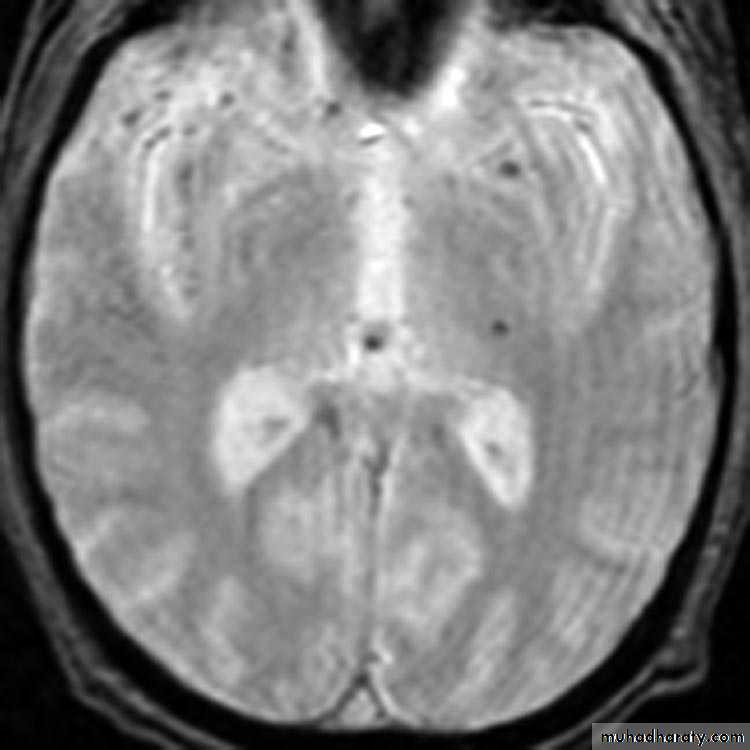
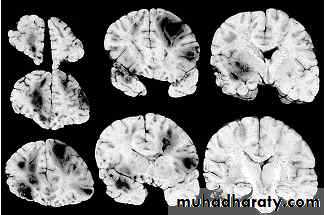
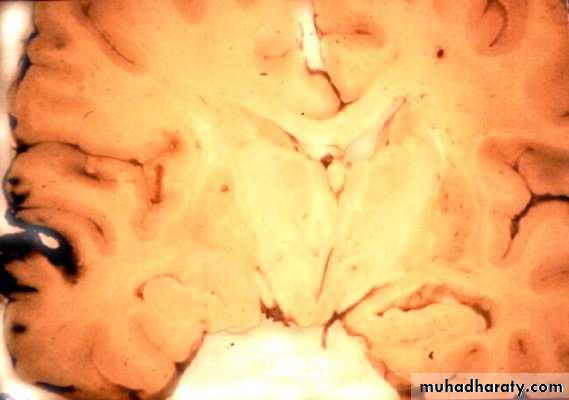
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
Prolonged post-traumatic state in which there is loss of consciousness from the time of injury that continues beyond 6 hours.Occurs as a result of mechanical shearing at the grey-white matter interface.
This causes disruption and tearing of axons, myelin sheaths and blood capillaries.
Severity can range from mild damage with confusion to coma and even death.
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
1. Diffuse Axonal Injury
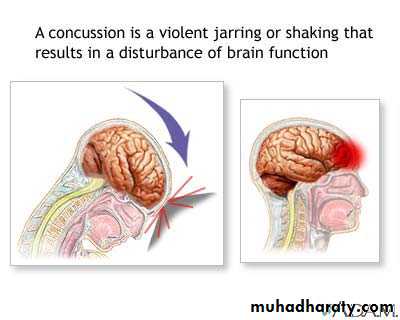
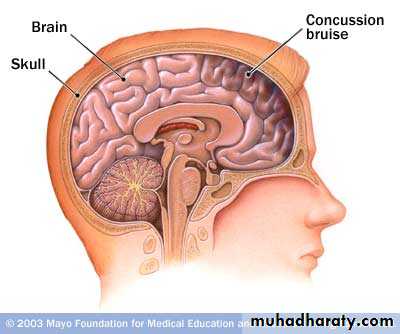
2. Cerebral Concussion
There is slight brain distortion.This is a clinical diagnosis, and is manifested by temporary cerebral dysfunction.
Latin (concutere) means shake.2. Cerebral Concussion
The clinical presentations includes:1. Autonomic abnormalities including bradycardia, hypotension and sweating
2. Loss of consciousness often but invariably accompanies concussion.
3. Amnesia of events is common.
4. Temporary lethargy.
5. Irritability.
6. Cognitive dysfunction.
2. Cerebral Concussion
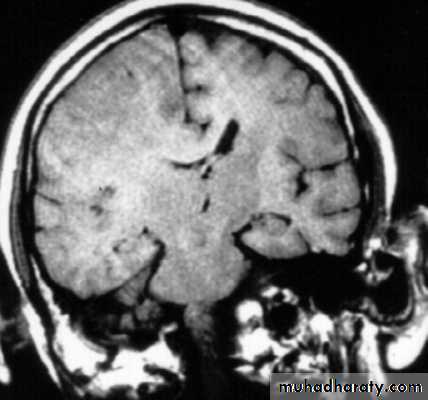
3. Brainstem and hemispheric (Cerebral) Contusion
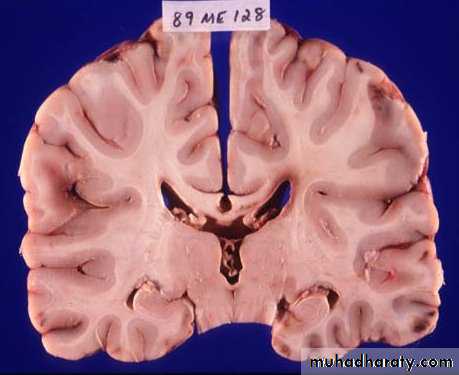
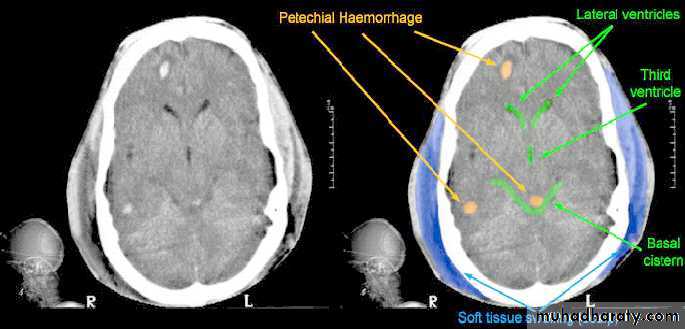
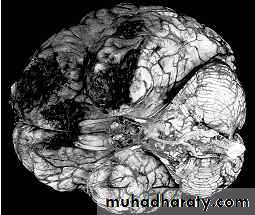
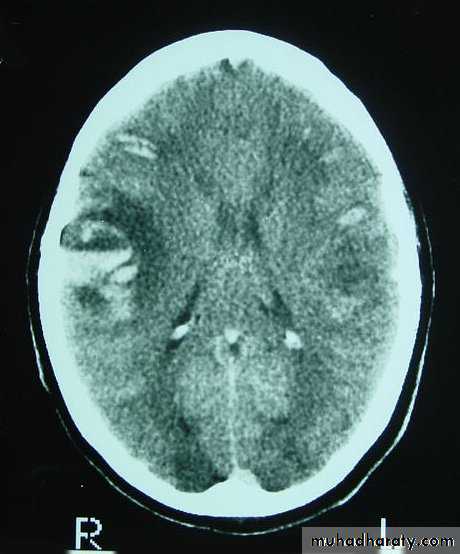
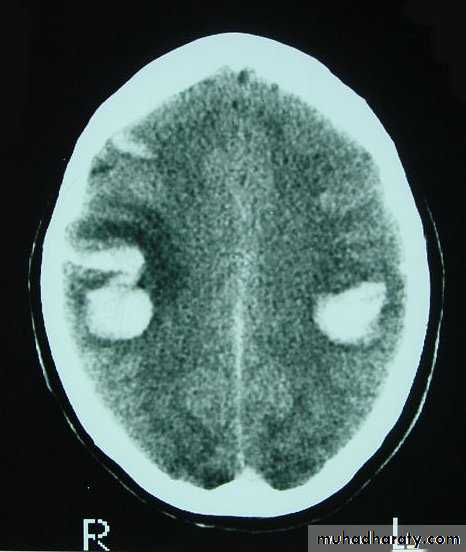
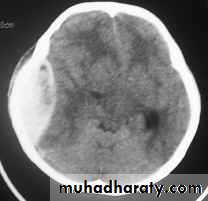
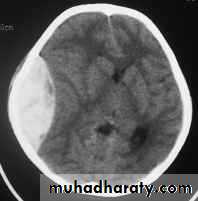
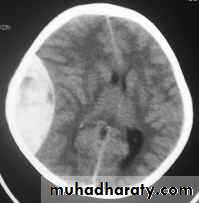
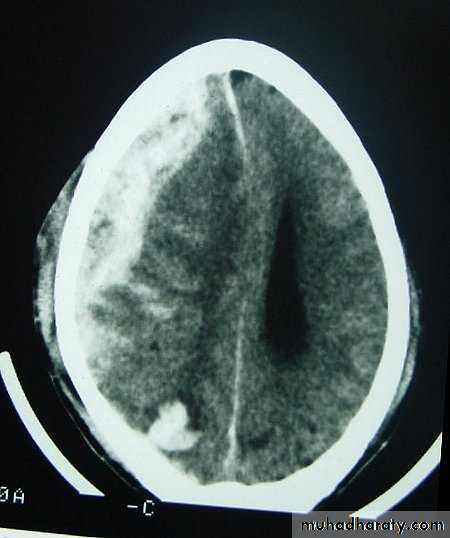
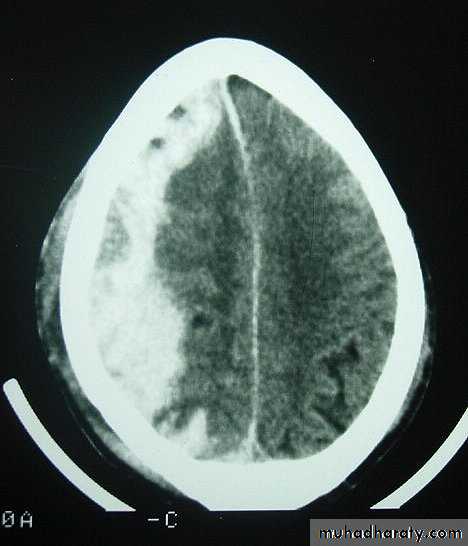
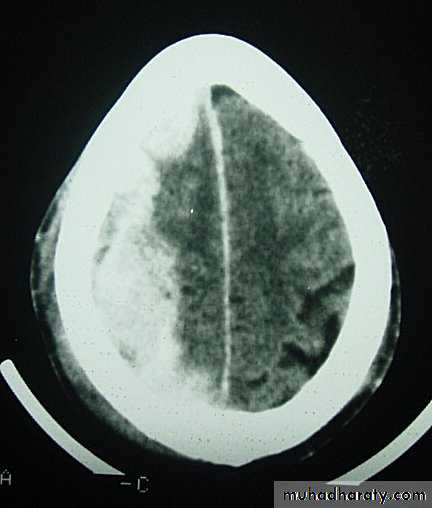
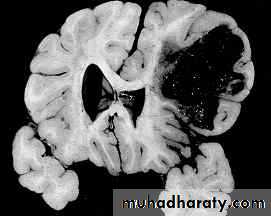
These are areas of bruising and swellings with intact pia arachnoid, localized or generalized oedema and haemorrhage due to tearing of blood vessels.3. Cerebral Contusion
Clinical presentations:1. Prolonged periods of unconsciousness.
2. Focal neurological deficits that persist for longer than 24 hours.
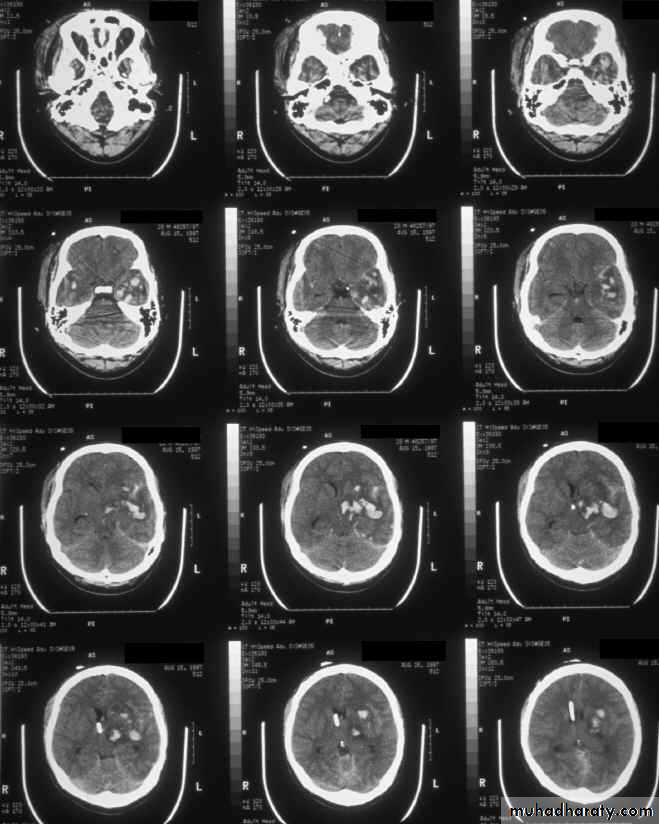
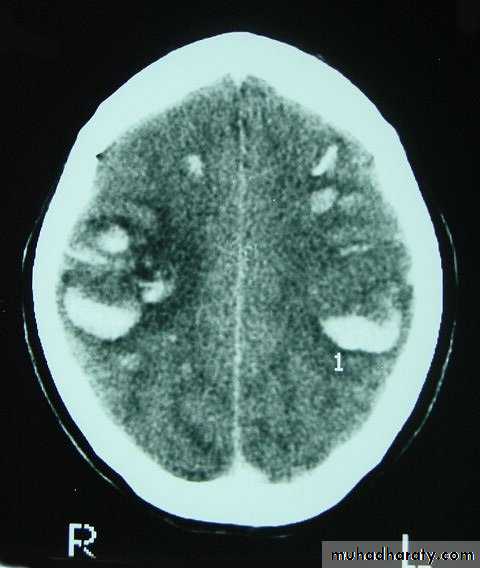
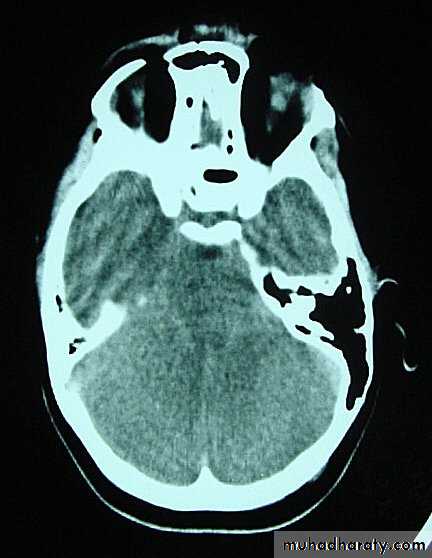
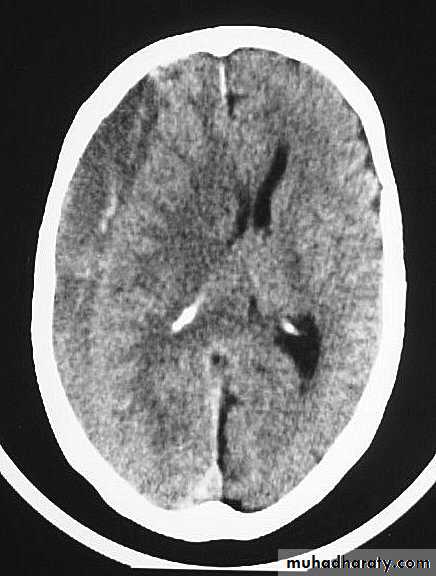
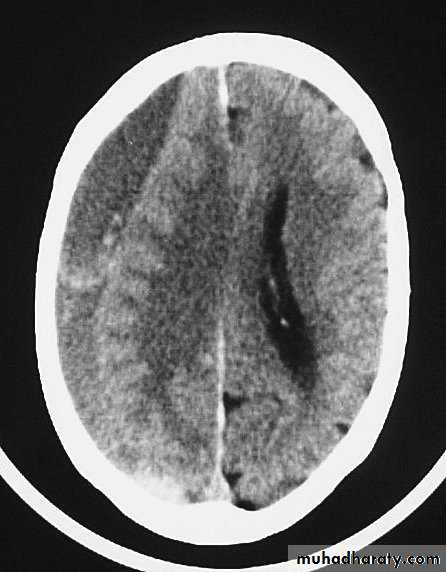
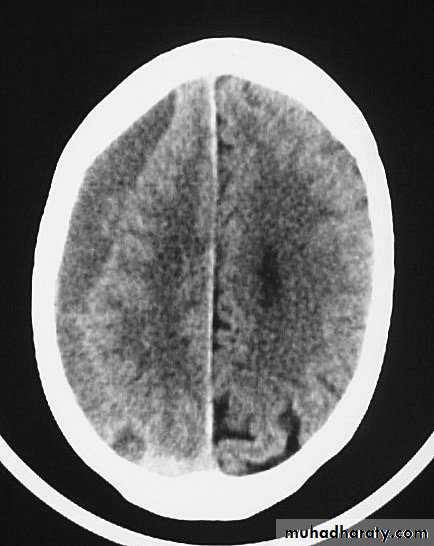
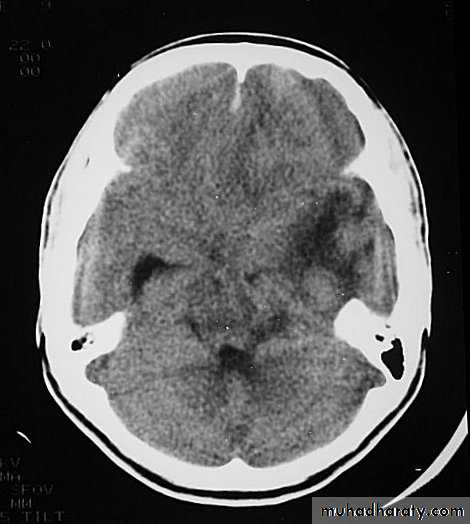
CT scans demonstrates contusions as small areas of haemorrhage in the cerebral parenchyma.
Contusions may resolve with the accompanying deficits or they may persist.
3. Cerebral Contusion
3. Cerebral Contusion
3. Cerebral Contusion
3. Cerebral Contusion
3. Cerebral Contusion
Resolution of Contusion
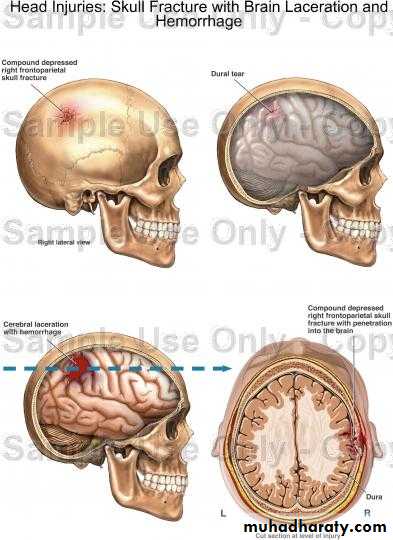
4. Cortical Lacerations
It is due to rapid movement and shearing of brain tissue.The pia arachnoid is torn, with bloody effusion in the CSF.
Intracerebral haemorrhage may accompany this lesion.
Focal deficits are the rule.
4. Cerebral Laceration
II. Secondary Brain Injury
• Brain Oedema (Cerebral Swelling).• Intracranial Haemorrhages.
• Infection.
• Seizures.
• Hydrocephalus.
• Vascular Changes (Cerebral ischemia).
• Cerebral Herniation.
• CSF Rhinorrhoea.
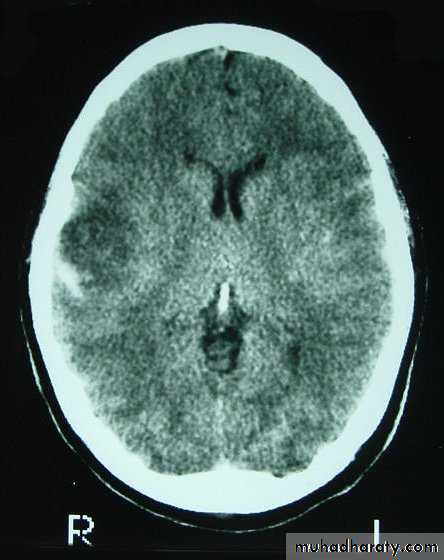
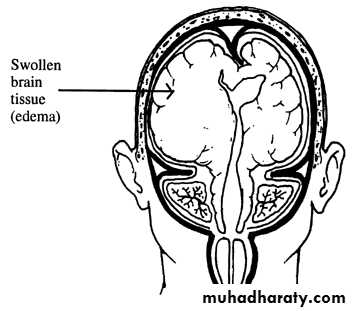
1. Brain Oedema (Cerebral Swelling)
Can be local (around a haematoma) or diffuse.
It is due to intracellular or extracellular accumulation of fluid.
It leads to raised intracranial pressure, which itself causes problems.
It is more common and more dangerous in children.
1. Brain Oedema (Cerebral Swelling)
1. Brain Oedema (Cerebral Swelling)
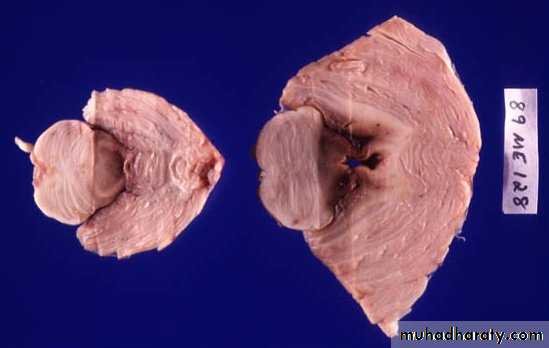
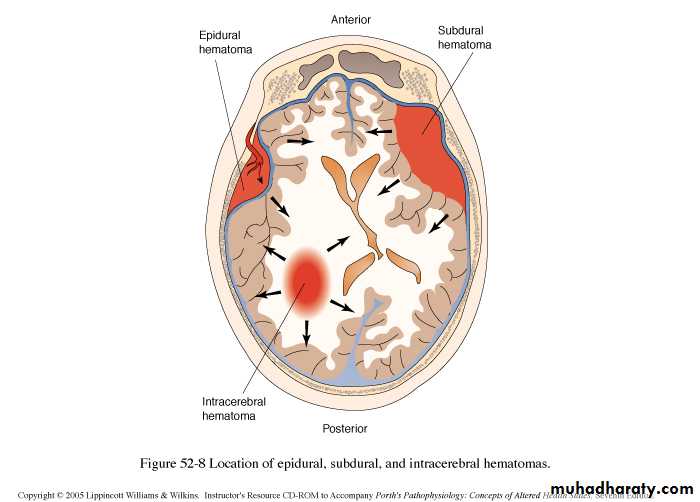
2. Intracranial Haemorrhages
a. Extradural Haematomab. Subdural Haematoma: acute or chronic
c. Intracerebral Haematoma
d. Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
2. Intracranial Haemorrhages
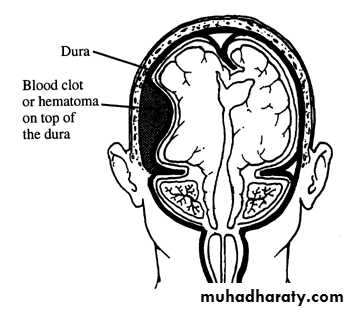
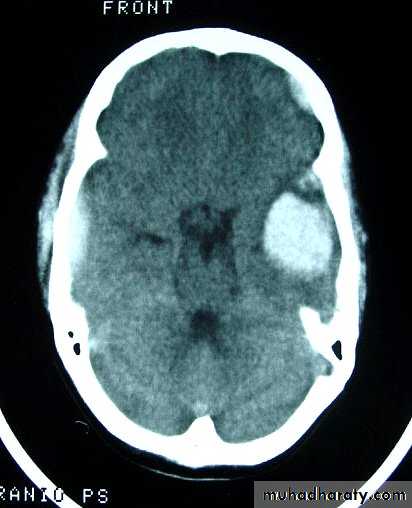
a. Extradural Haematoma
Usually due to TRIVIAL trauma.Source of bleeding(Haematoma):
1. Linear squamous temporal skull fractures with laceration of a branch of the underlying middle meningeal artery.2. Fractured bone edges.
3. Laceration of the dural sinuses.
a. Extradural Haematoma
Clinical Picture; includes:Stage of concussion.
Stage of lucid interval
Stage of compression: shown clinically as:
Gradual progressive deterioration in the level of consciousness.
Contralateral hemiparesis due to cortical compression.
Tentorial herniation, with compression of oculomotor nerve, with dilatation of ipsilateral pupil.
As the coma deepens the blood pressure rises and the pulse and respiration slow down (i.e. features of increased intracranial pressure).
a. Extradural Haematoma
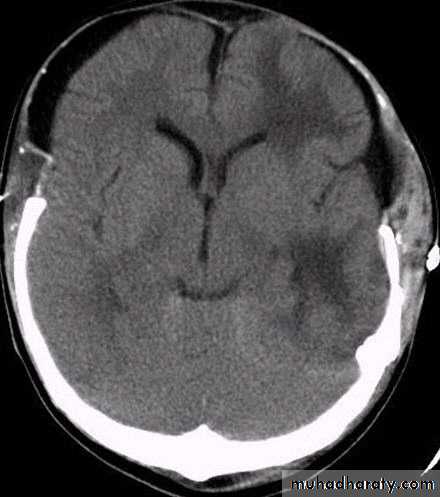
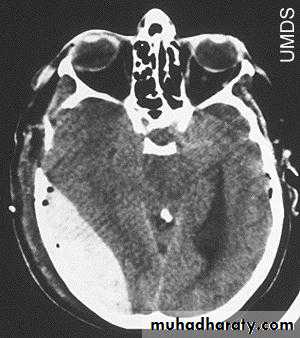
CT scan will show biconvex or lens configuration.
They are more likely to occur in the younger age group.
An extradural haematoma is a neurosurgical emergency.
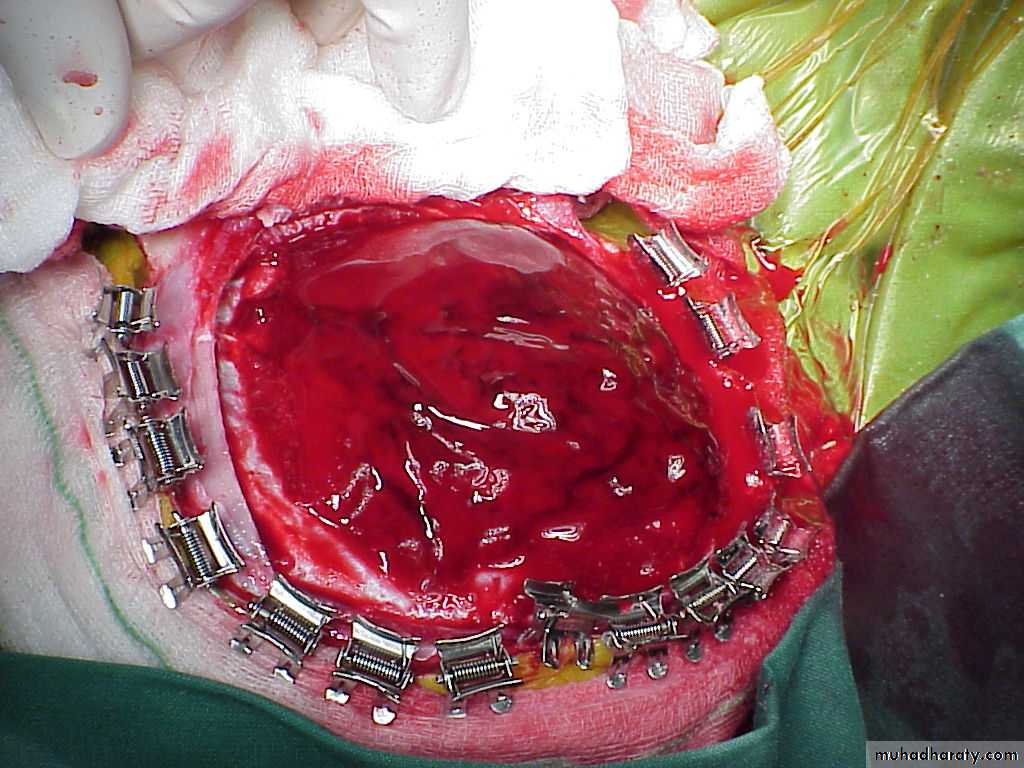
Surgical treatment by evacuation of haematoma via CRANIOTOMY.
Care must be taken in assessing patients with linear fractures crossing the middle meningeal territory.
a. Extradural Haematoma
a. Extradural Haematoma
a. Extradural Haematoma
a. Extradural Haematoma
a. Extradural Haematoma
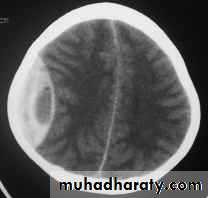
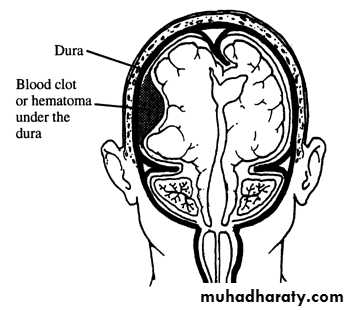
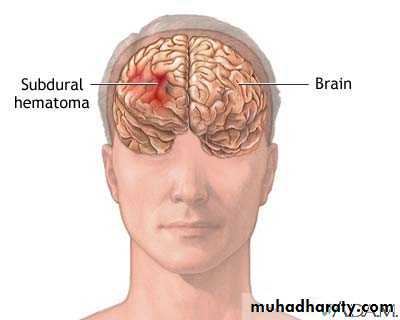
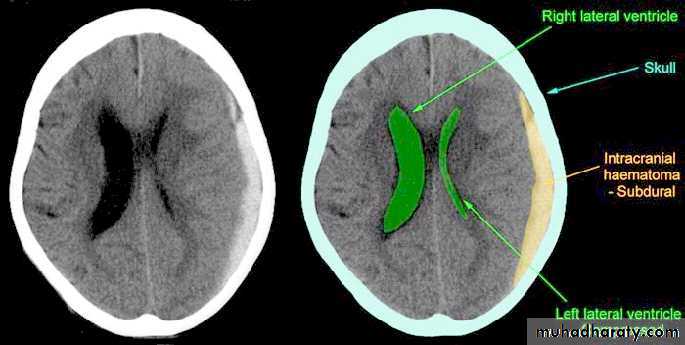
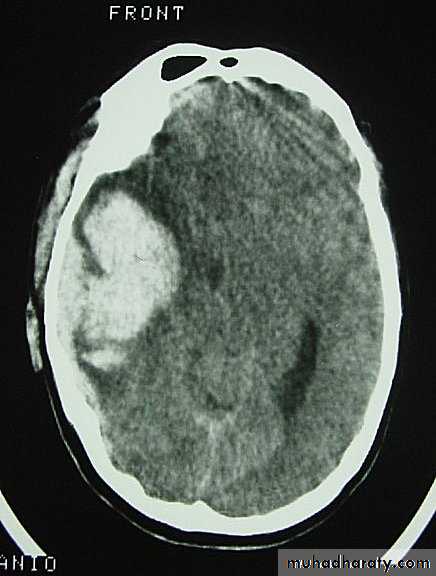
b. Subdural Haematoma
They are the most common intracranial mass lesions resulting from head trauma.They are classified depending on how long they take to present clinically following the injury into:
Acute Subdural Haematoma: less than 3 days
Subacute Subdural Haematoma: 4-21 days
Chronic Subdural Haematoma more than 21 days.
b. Subdural Haematoma
b. Subdural Haematoma
b. Subdural Haematoma
b. Subdural Haematoma
Acute Subdural Haematoma
Usually due to MORE SEVER high velocity trauma and thus associated with a poorer outcome.Source of bleeding (haematoma): include:
Most result from torn bridging veins or focal tears of a cortical artery.
Cortical lacerations or contusions.
Bleeding from tears in the dural venous sinuses.
Acute Subdural Haematoma
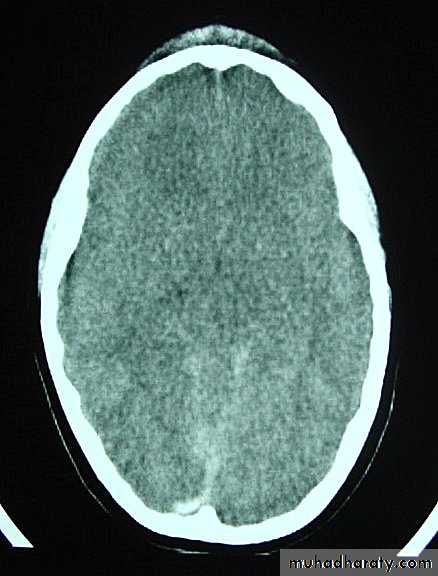
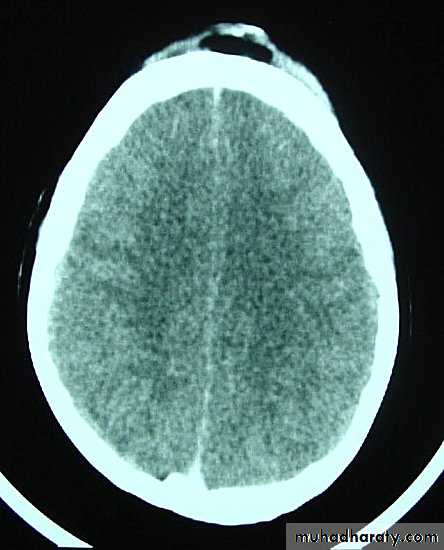
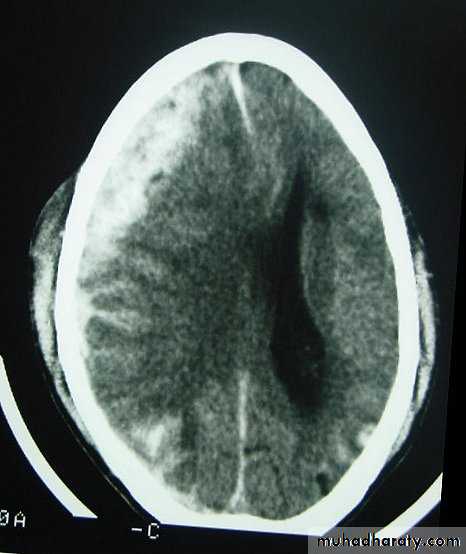
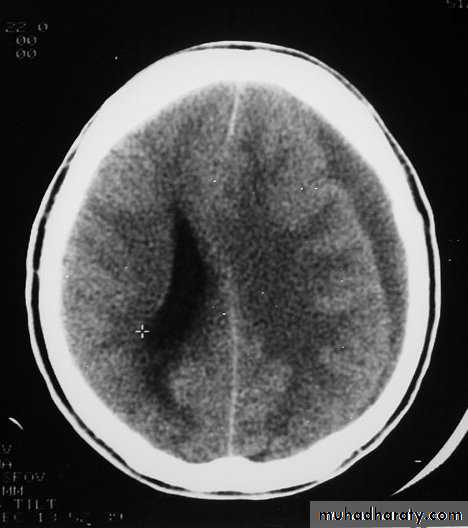
Clinical Picture: patient will present with a picture similar to that of an extradural haematoma, but there is persistent loss of consciousness with no lucid interval.Ct scan will show a concave hyperdence collection because blood follows the subdural space over the convexity of the brain.
Acute Subdural Haematoma are rapidly evolving lesions and early evacuation via craniotomy is mandatory.
Acute Subdural Haematoma
Subacute Subdural Haematoma
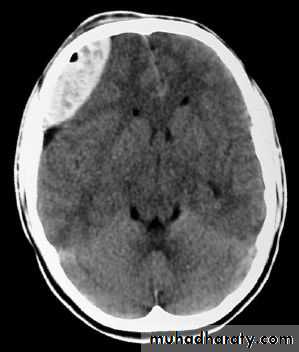
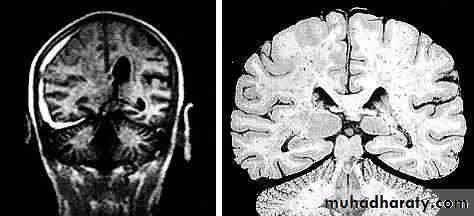
Chronic Subdural Haematoma
Most common in infants and in adults over 60 years of age secondary to SLIGHT blow to the head which may pass unnoticed.Source of bleeding (haematoma): usually from bridging veins as they pass to the venous sinuses.
The patients present with progressive neurological deficits more than 3 weeks after the trauma.
The initial head injury is often completely forgotten.
Chronic Subdural Haematoma
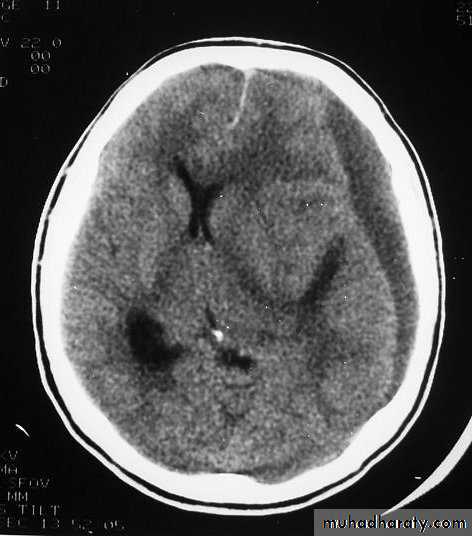
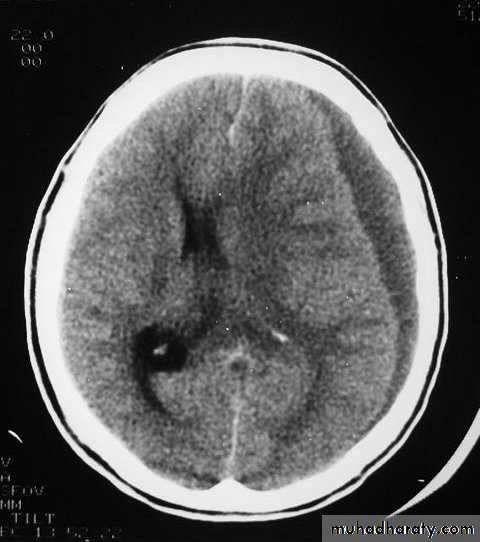
CT scan: the acute clotted blood is initially appears white (hyperdence), but as it liquefies, it slowly becomes black (hypodense).
They should be drained if they continue to enlarge.
They are evacuated by drilling burrholes over the collection and washing it out with warmed saline.
Chronic Subdural Haematoma
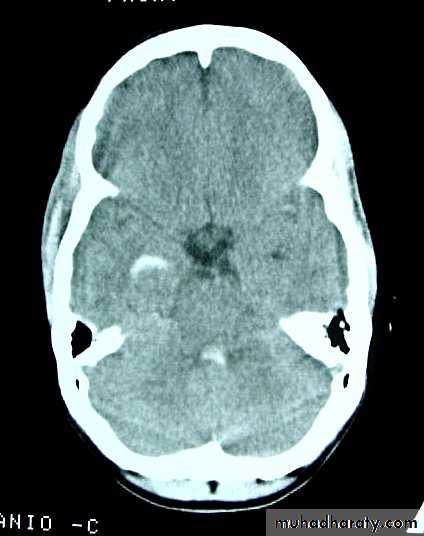
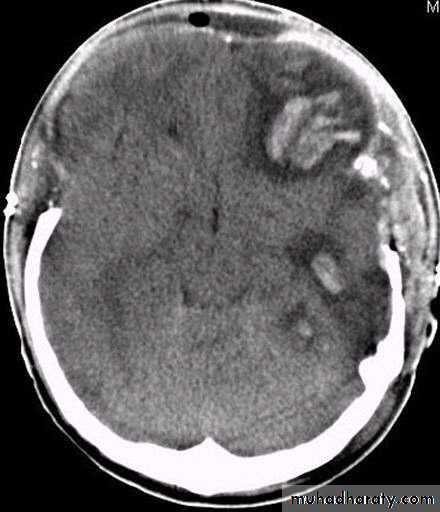
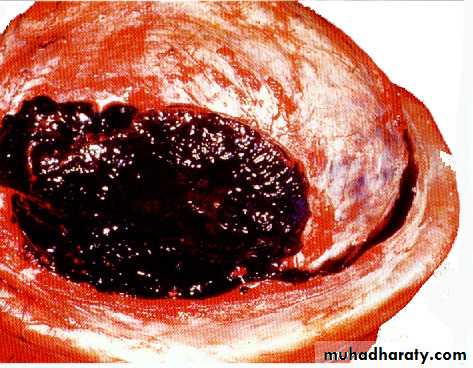
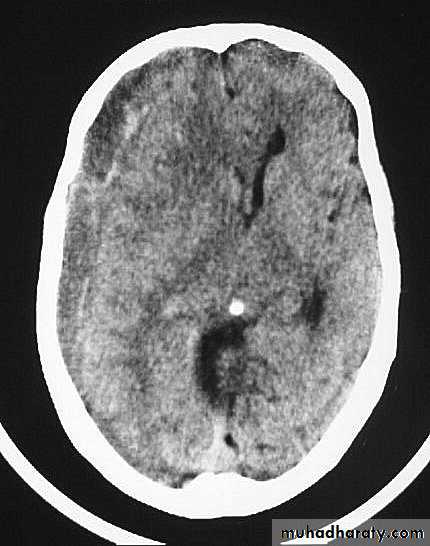
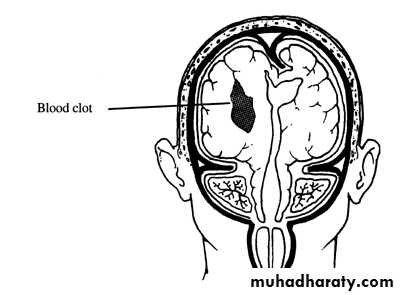
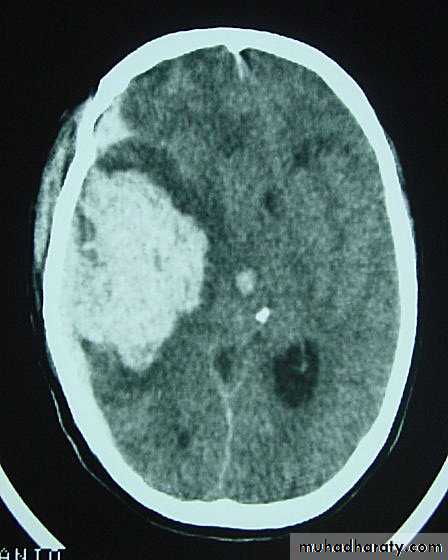
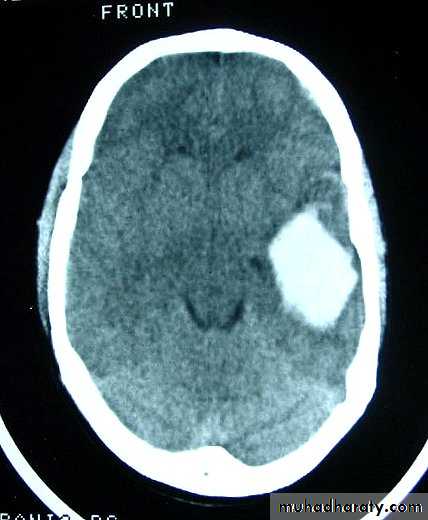
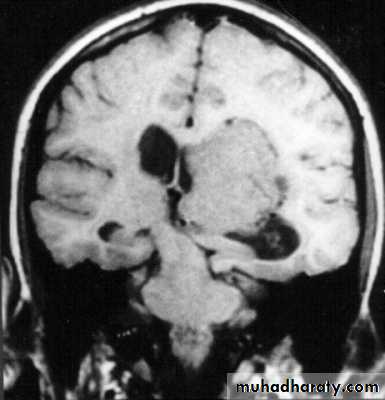
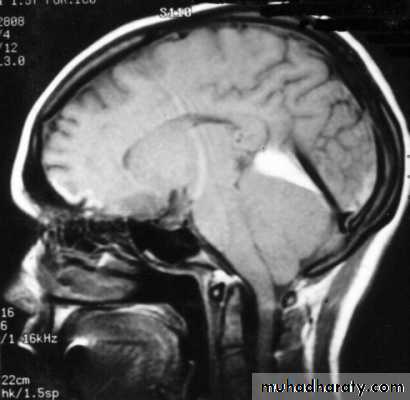
c. Intracerebral Haematoma
This is the least common of traumatic haematoma.They are due to areas of traumatic contusion coalescing into a contusional haematoma.
Disrupted cerebral tissue release thromboplastins that potentiate haemorrhage.
c. Intracerebral Haematoma
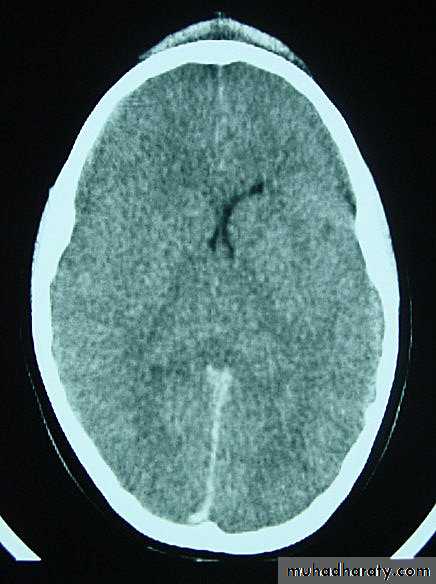
CT scan: appear as hyperdence lesions with associated mass effect and midline shift.Large intracerebral haematomas should be evacuated unless the patient’s neurological state is improving.
Small inracerebral haematomas may not require removal, but be aware that they can expand.
c. Intracerebral Haematoma
c. Intracerebral Haematoma
c. Intracerebral Haematoma
d. Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
Trauma is the commonest cause of SAH although aneurysms are the most common cause of spontaneous SAH.Traumatic SAH is managed conservatively.
3. CNS Infection
Causes: includes:
1. Penetrating skull trauma.
2. Depressed skull fractures.
3. Base of skull fractures.
All these will provide portal for CNS infection.
3. Infection
Presentations: either:1. Meningitis.
2. Brain abscess.
3. Subdural empyemas.
These can all exacerbate situation of raised intracranial pressure.
4. Seizures
They can increase both brain metabolism and blood flow, therefore increasing intracranial pressure.5. Hydrocephalus
a. Acutely due to obstruction of CSF outflow due to intraventricular blood.b. Delayed post-traumatic communicating hydrocephalus due to impaired CSF reabsorption following traumatic subarachnoid haemorrhage
Intraventricular blood can lead to Hydrocephalus
6. Vascular changes (cerebral ischemia)
This occurs after sever head trauma and is caused by hypoxia, impaired cerebral perfusion or both.The injured brain loses its ability to autoregulate, and so be unable to maintain cerebral blood flow with a decreased blood pressure.
Toxic chemicals accumulation like glutamate and free radicals will lead to neuronal damage.
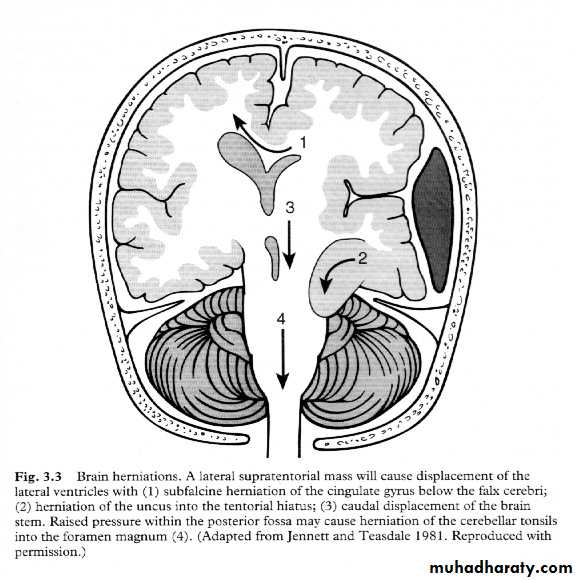
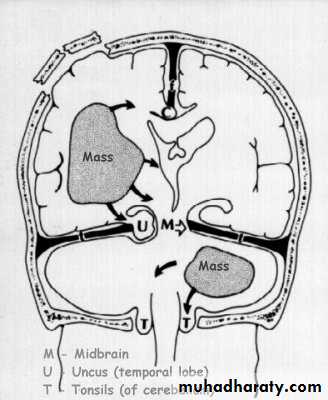
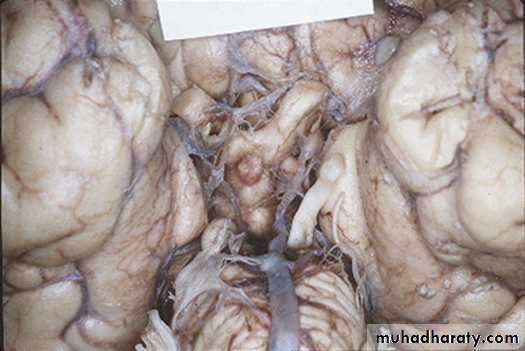
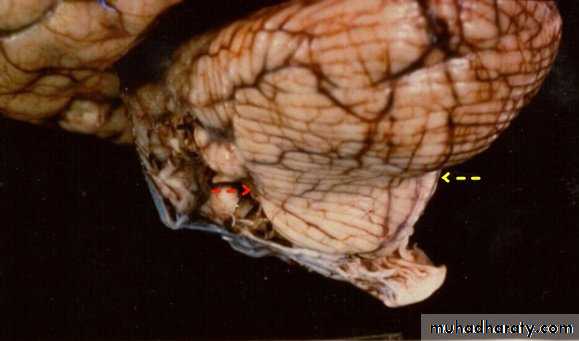
7. Cerebral Herniation
a. Subfalcine Herniationb. Uncal Herniation
c. Tentorial Herniation
d. Tonsillar Herniation
7. Cerebral Herniation
7. Cerebral Herniation
a. Transtentorial Herniation
a. Transtentorial Herniation
b. Foramen magnum herniation
b. Foramen magnum herniation
c. Subfalcine Herniation
c. Subfalcine Herniation
8. CSF rhinorrhoea
Occurs secondary to a fracture involving the paranasal sinuses (frontal, ethmoidal or sphenoid) associated with dural tear.A piece of brain tissue is forced into the dural tear and prevents its healing.
This complication is liable to be followed by meningitis.
8. CSF rhinorrhoea
The patient is treated early with antibiotics.Indications for surgery (repair of tear) includes:
a. Persistence of rhinorrhoea more than 10 days
b. Presence of a fracture involving the frontal or ethmoidal sinus.
c. Occurrence of meningitis.