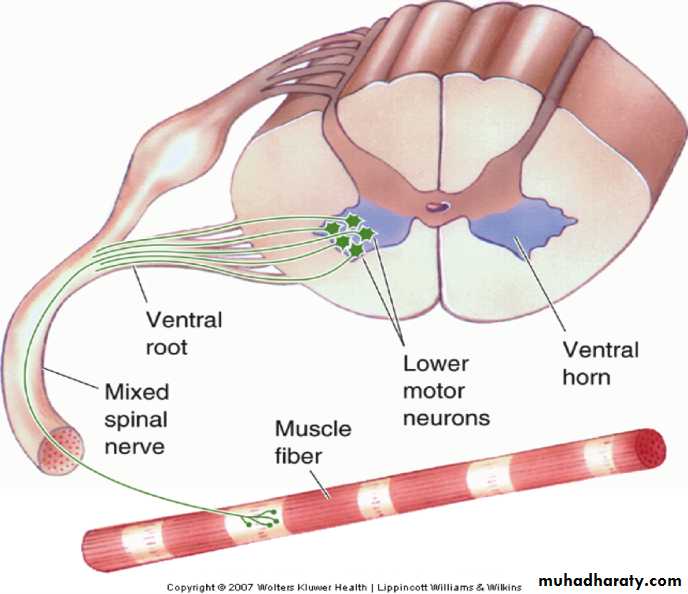
Anatomical Tracts
1- Motor system2- Somatic –sensory system
Lobes of brain
Frontal lobePersonality
Emotional control
Social behaviour
Contralat. Motor control
Language
Micturition
Parietal Lobe
Dominant Non_domin
Language spatial orientation
Temporal LobeAuditory perceptionLanguageVerbal memorySmellAuditory perceptionMelody perceptionNon-verbal memorySmellDominantNon_dominantCalculation constructional skills
Occipital Lobe
Visual processing
INVESTIGATIONS
A-tests of function:
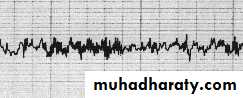
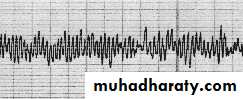
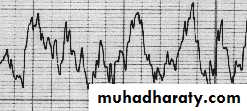
1-Electroencephalography(EEG):
1% of brain activity
Beta >13/sec.
Alpha 7-13/sec.
Theta 4-6/sec.
EEGAlpha 8-13 HzBeta > 13 Hz Theta 4-7 HzDelta < 4 HzFREQUENCYAMPLITUDE < 5 mV5-15 mV10-50 mV> 50 mV
Dr. Estabrak AlyouzbakiDelta <4/sec.
Abnormalities of EEG
1-Abnormal waves:
Spikes, sharp & slow waves.
2-Patteren:
i-continuous
ii-episodic.
iii-focal.
iv-diffuse.
Fp1-F7F7-T3T3-T5Left Temporal SpikesSpike and slow wave complex
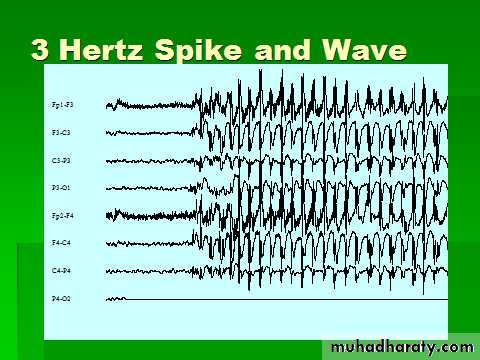
Generalized Spike-Wave
Generalized Delta Slowing
EEG & EPILEPSY
1-Diagnosis.
2-Management.
3-Distinguish between types of epilepsy.
4-Surgical treatment of epilepsy.
EVOKED POTENTIALS
Definition.
Types:
1-Visual EP. (VEP)
2-Brainstem or Auditory EP.(BEP)
3-Somatosensory EP.(SSEP)
Electromyography & Neurography
EMG:
1-Spontonous activity.
2-Motor unit potential.
3-Interference pattern.
Indications & Uses:
1-Muscle diseases.
2-Neuromuscular junction study.
3-Denervation pattern detection.
Electroneurography
1-MNCV.
2-SNCV.
3-MAP.
4-SAP. .
USES: for detection the following:
1-Damage to peripheral nerves.
2-Focal or diffuse lesion.
3-Axonal or demyelinating type of lesion.
4-Nerve root study.
NEURORADIOLOGY
I-Skull and Spine Plain X ray:
This is used for detection:
1-traumatic lesion like fractures.
2-boney lesions; metastases,osteomylitis,Pagets’disease.
3-sella turcica enlargement or destruction.
4-Intracranial calcefications;oligodendroglioma, Aneurysem,sturge-weber.
5-signs of raised I.C.P.
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
Value & Indications:
1-I.C. S.O.L.
2-I.C.Vascular lesions; hemorrhage, infarction, sub&extradurahematoma, SAH.
3-Ventricular system study.
4- Brain atrophy.
Limitations of CT scan
1-lesions smaller than one cm.
2-Posterier fossa lesions
3-Spinal cord .
4-Bone artifact or overlap
MRI AND MRA
ADVANTAGES;
1-distinguishe between white and gray matter.
2-direct images of spinal roots and cord.
3-resolution is greater than CT.
4-no radiation.
5-MRA doesn't need contrast.
6-better detection of intracerebral, posterior fossa and plaques lesions.
LIMITATIONS
1-time consuming.
2-costly.
3-claustrophobia
4-prsence of metallic things in the body.
5- overweight.
OTHER RADIOLOGICAL INVESTIGATIONS
1-Angiography; carotid , VBasilar andDigital subtraction angiography.
2-Ultrasound; Doppler imaging of blood vessels.
3-Myelography.
4-Isotopic brain &bone scanning.
5-Positron emission tomography(PET).
6-Single photon emission computed Tomography (SPECT).
BIO CHEMICAL ,BLOOD AND OTHER TESTS
1-Serum glucose,urea,electrolytes,calicum…etc
2-TFT.
3-Muscle enzymes( CPK , LDH ,SGOT).
4-CBC and film, urine ex.
5-CXR.
6-CSF examination.
7-Gentic study.
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF)
Indications for lumbar puncture:1-In the diagnosis of; meningitis,encephalitis,SAH,M.S.,neoplastic infiltration
2-Intrathecal therapy.
3-Myelography.
4-Diagnosis and treatment in B.I.H.
CONTRAINDICATIONS OF L.P.
1-Brain or spinal cord mass.
2-Raised I.C.P.and presence of papillodema.
3-Local infection.
4-Congenital lesion in lumbosacral area.
5-Clotting abnormalities; thrombocytopenia anticoagulant therapy, bleeding tendency
6-Unconsious patient.
7-Presence of focal neurological deficit.
NORMAL CSFPressureColour Red cell countWhite cell countGlucoseProteinMicrobiologyOligoclonal bands150-180 mm water Clear0-4/mm30-4/mm3>60% of blood level<0.45g/lSterileNegative
BIOPSIES
1-NERVE: SURAL ,RADIAL N.; peripheral neuropathy(vasculitis,amyloid…).
2-MUSCLE:muscle dystrophy,myositis.
3-BRAIN.
By : younis alomary