Dental Instrument
Lecture 2
Dr. Samira Jameel JuhiDental Instrument
1-Hand powered dental instrument:-Carbon steel was the primary material used (harder and maintained sharpness than st.st.).Stainless steel is now preferred( remain bright with steam or dry heat sterilization).
Cutting Instrument
Non cutting InstrumentCutting Instruments
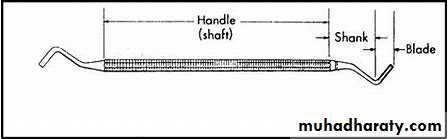
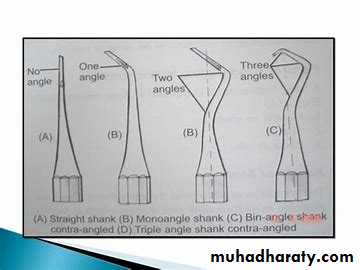
Blade or Nib: the working end of the instrument ,some of instruments have a blade on both ends of the handle ( double ended instruments).Shank; connect the handle to the blade may be with straight monoangle , bi angle, triangle, or quad angle the angle is important to keep the blade edge within 1-2mm to the long axis of instrument.
Handle: part grasped by the operator hand
Instrument formula by G.V. Black
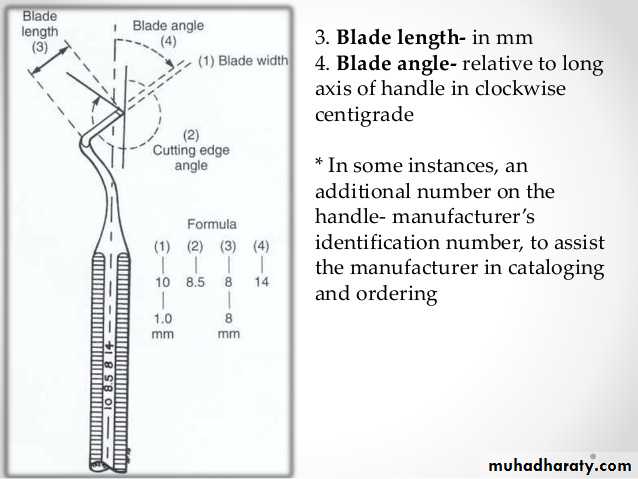
3 Number instrument formulaCutting edge at right angle to the blade
• Width of blade in tenth of millimeter.
• Length of blade in millimeter.
• Angle the blade forms with the axis of the handle in centigrade( example. 1.0,7,14 °) enamel hatchet formula
Instrument formula by G.V. Black
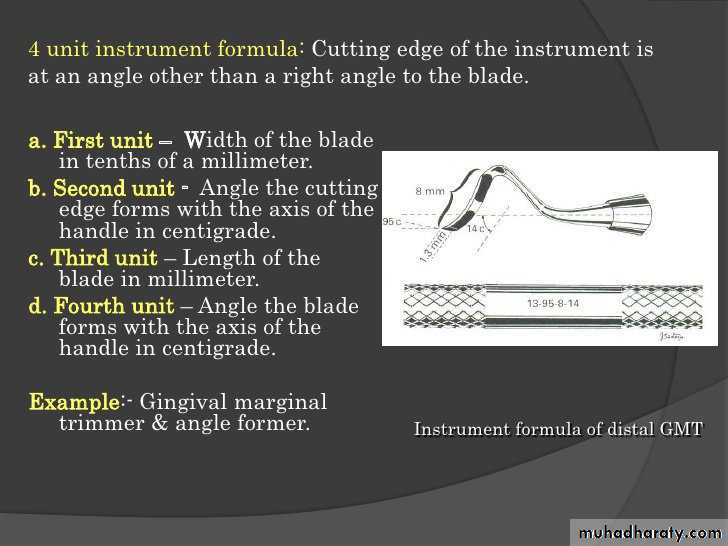
4 Number instrument formulaa. width of blade in tenth of millimeter
b. angle the cutting edge with the long axis of the handle in centigrade
c. length of blade in millimeter
d. angle the blade forms with the axis of the handle in centigrade( example. 1.3.95.8.14) gingival marginal trimmer formula
Cutting Instruments
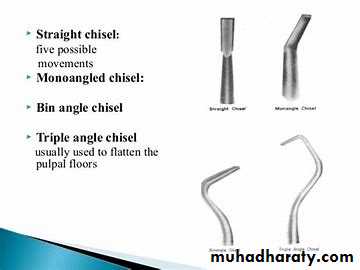
Chisel:Used for cutting E. or D.
Has either straight shank or slight blade curvature.
Its cutting edge is perpendicular to the axis of the handle
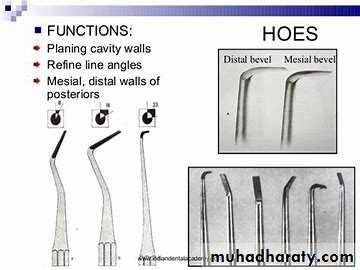
Hoe:
Its cutting edge is perpendicular to the axis of the handleThe same use as chisel
Hatchet:
Cutting edge parallel to the long axis of the handle and beveled only from one sideUsed for cutting E. ,D.
Come as right or left types
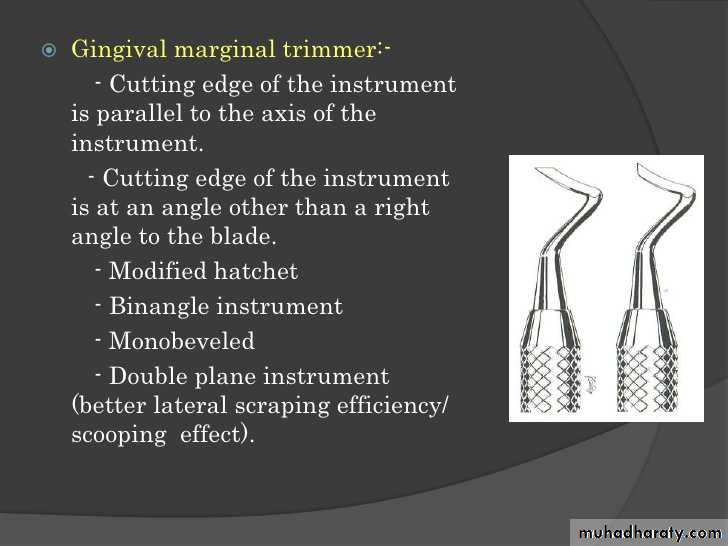
Gingival marginal trimmer
Beveling the gingival margin of proximo-occlusal preparation and axiopulpal line angle in CL II cavities.Spoon excavator:
The blade is curved and the cutting edge at the end of the blade in the form of a semicircle.Outer convexity and inner concavity that make it like a spoon
Non cutting instruments
Diagnostic instruments
Mirror
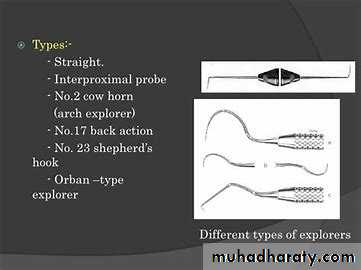
Probe or explorer
Tweezer
Plastic instruments
Ash6
Ash49
Dycal applicator
Cement spatula
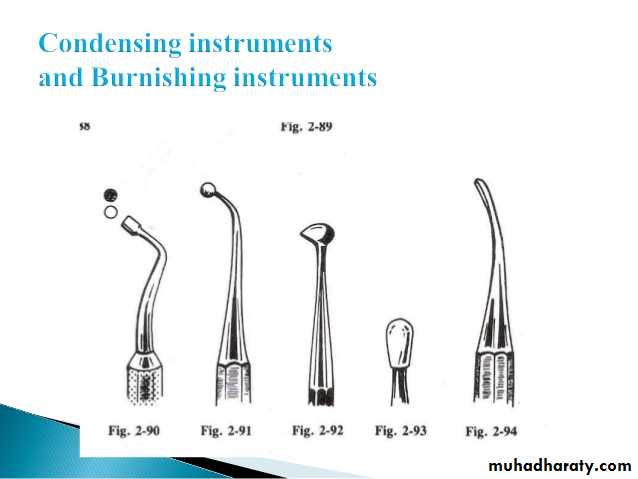
Amalgam instruments
Condenser :compress the amalgum in to al area of cavity.Burnisher: nib shape round ,oval, or rounded cone. Burnish the amalgum on the margin of cavity also smoothing of carved amalgam surfaces.
Caver: shape the amalgum or resin composite.
Amalgum carrier: carry the amalgum and place it in to the prepared cavity.
Rotary instruments
Hand piecesStraight: used more in laboratory work
Contra angle :in mouth
1-low speed-Hand pieces
500-15,000 rpm( revolution per minute) used to removed carious dentine, finish the prepared cavity.
2- High speed- hand piece : 160,000 rmp and some have speed up to 500,000 rmp.
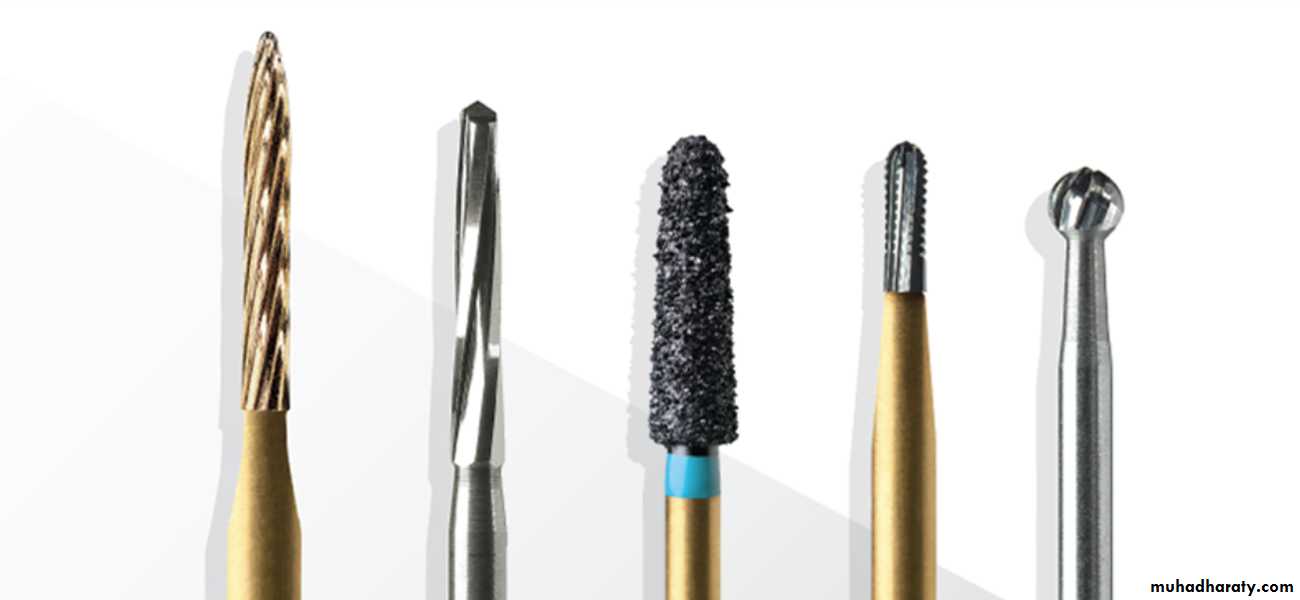
Burs
A group of instruments that can turn on an axis with different speed of rotation to perform different types of work.
1. Cutting
2. Abrasive
3. Finishing
4. Polishing
Burs used for cutting are manufactured from different materials:
1. Stainless steel.2.Carbide.
3.Diamond.
Each bur consist of three parts:
1.Shank: part that fit into handpiece.2.Neck: part connects head to the shank.
3.Head: working part of the bur.
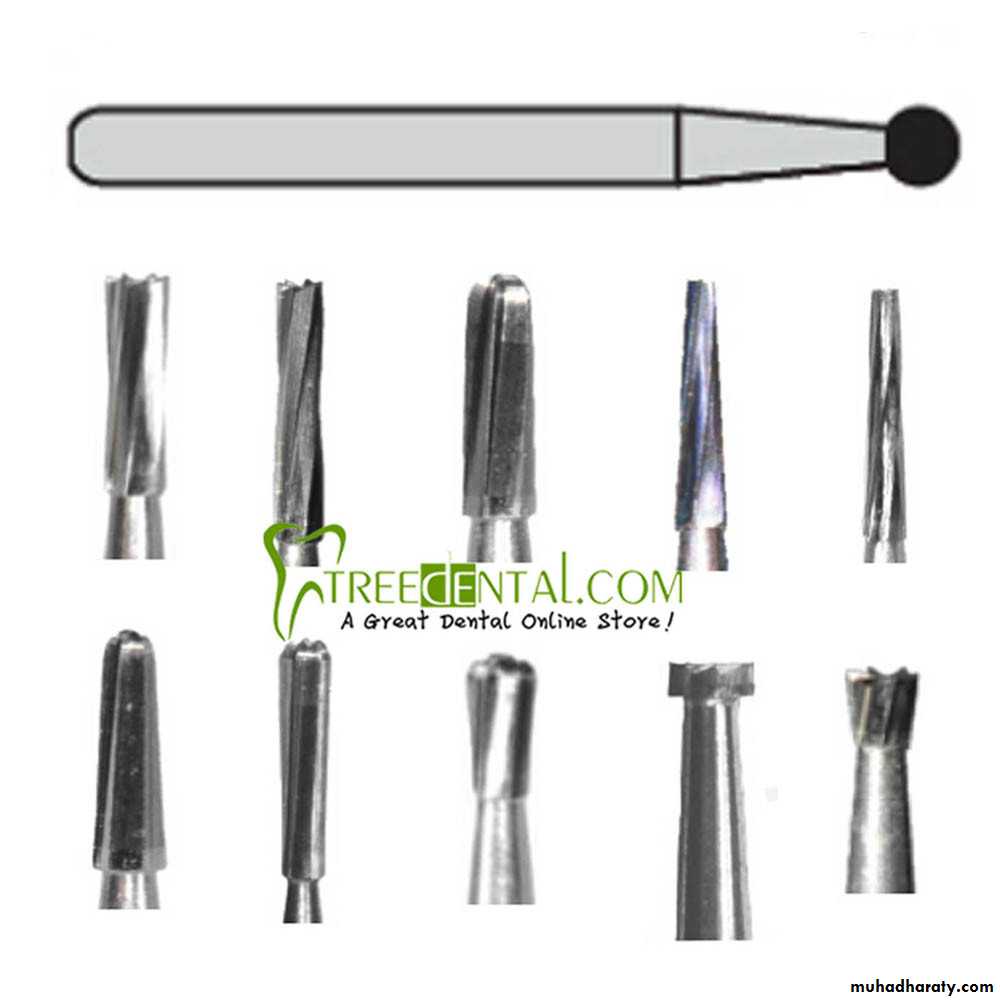
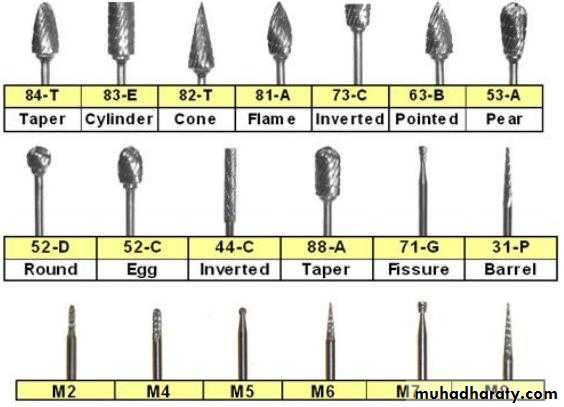
Types of Burs
The burs have hundreds of shapes and sizes. The basic bur shapes:1. Round bur: the head is spherical so it is used for initial entry into the tooth, preparation of retentive holes or removal of caries dentin.
2. Inverted Cone bur : the head is a cone-shape with apex of cone directed toward the bur shank used for flatting the floor of the cavity, increasing the depth of cavity or for providing undercuts in cavities.
Fissure bur: elongated cylindrical head bur used for obtaining the outline form of the cavity and to cut walls, floor, or margins of the cavity , we have:
1.straight
2. tapered