NERVOUS SYSTEM
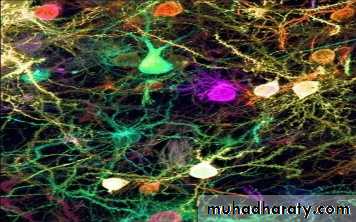
INTRODUCTION TO NERVOUS SYSTEMHistology of Nervous Tissue
2 types of cells
Neurons
Structural & functional part of nervous system
Specialized functions
Neuroglia (glial cells)
Support & protection of nervous system
Neurons
Function
Conduct electrical impulses
Structure
Cell body
Nucleus with nucleolus
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasmic processes
Dendrites
Axon
Basic functional unit of N.S.
Specialized cell
All cells have same basic properties
information processing
Transmits
Integrates
Stores
Regulation of behavior ~
Nervous Tissue: Neurons
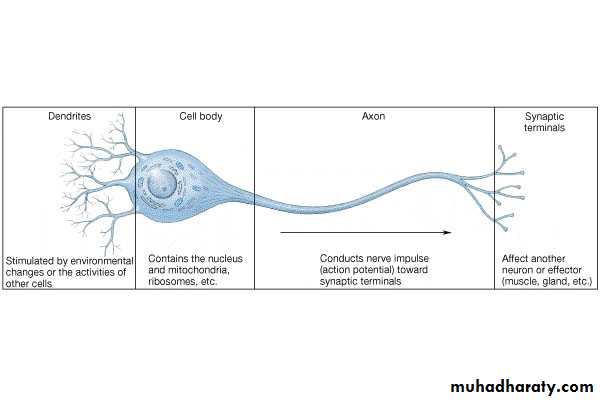
Neurons = nerve cellsCells specialized to transmit messages
Major regions of neurons
Cell body – nucleus and metabolic center of the cell
Processes – fibers that extend from the cell body (dendrites and axons)
Neuron Cell Body Location
Most are found in the central nervous system
Gray matter – cell bodies and unmylenated fibers
Nuclei – clusters of cell bodies within the white matter of the central nervous system
Ganglia – collections of cell bodies outside the central nervous system
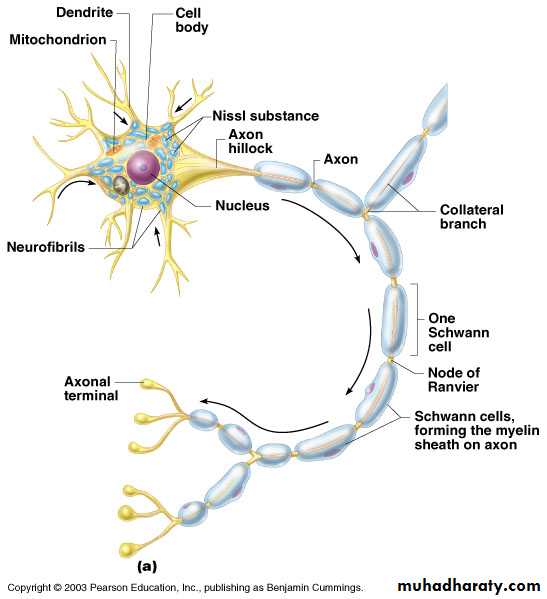
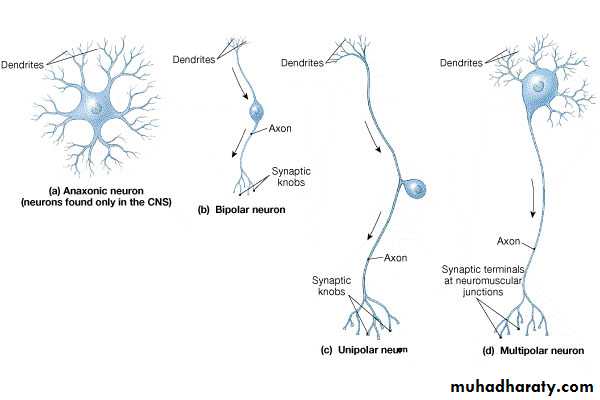
Neuron Anatomy
Cell body
NucleusLarge nucleolus
Extensions outside the cell body
Dendrites – conduct impulses toward the cell body
Axons – conduct impulses away from the cell body (only 1!)
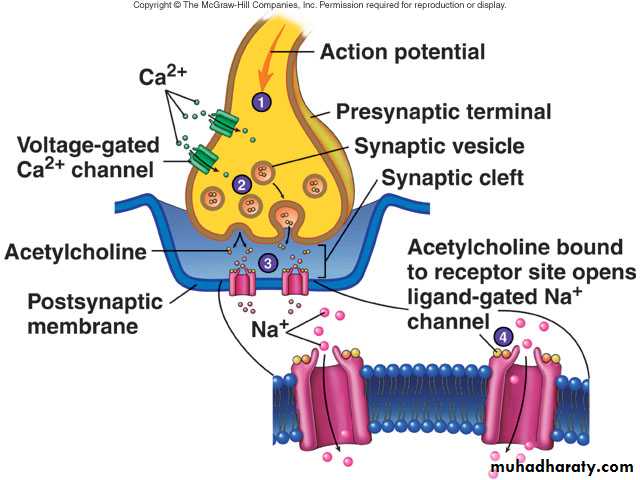
Axons and Nerve Impulses
Axons end in axonal terminals
Axonal terminals contain vesicles with neurotransmitters
Axonal terminals are separated from the next neuron by a gap
Synaptic cleft – gap between adjacent neurons
Synapse – junction between nerves
Chemical Synapses
Why are neurons connected?
Are all neurons equal in size?
Brain vs spinal cord vs peripheral nerves?
About how many neurons are in the human brain? 100 billions
About how many neurons are in the spinal cord? 1 billion
How long do you think the longest axon in the world is? around 15 feet
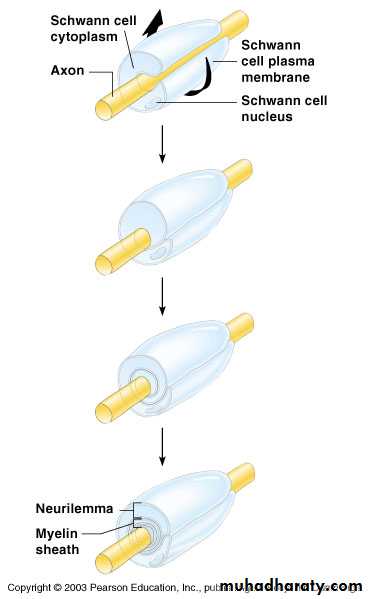
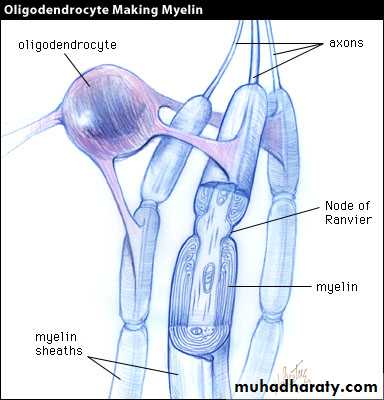
Nerve Fiber Coverings
Schwann cells – produce myelin sheaths in jelly-roll like fashion
Nodes of Ranvier – gaps in myelin sheath along the axon
Functional Classification of Neurons
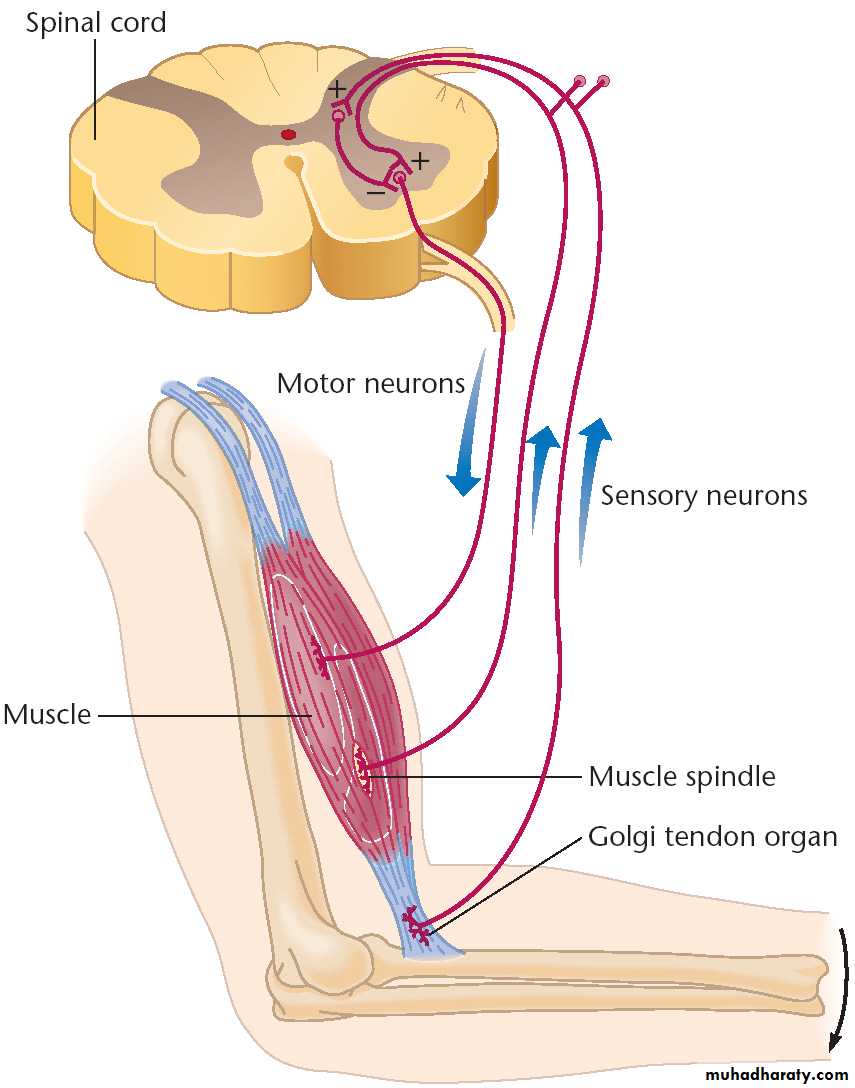
Sensory (afferent) neurons
Carry impulses from the sensory receptors
Cutaneous sense organs
Proprioceptors – detect stretch or tension
Motor (efferent) neurons
Carry impulses from the central nervous system
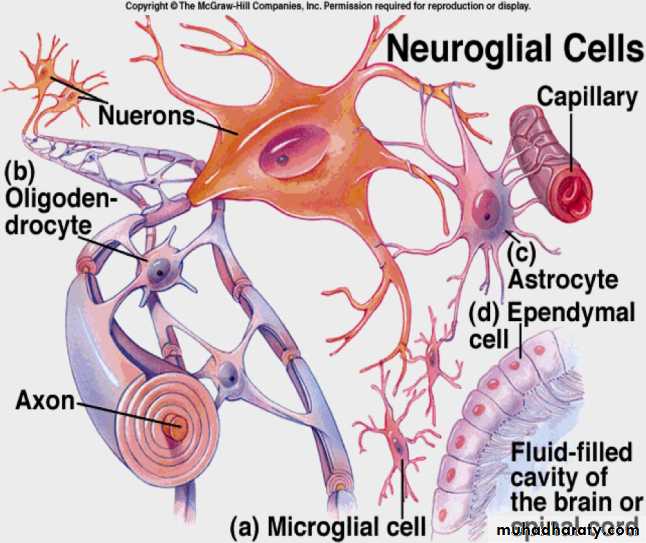
Neuroglia
Neuroglia of CNS
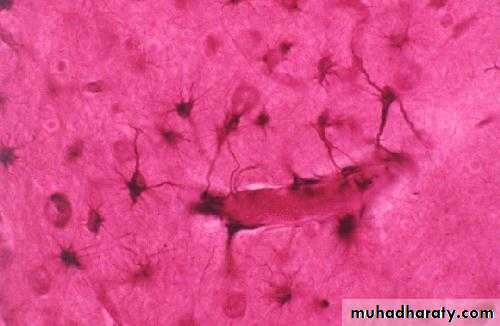
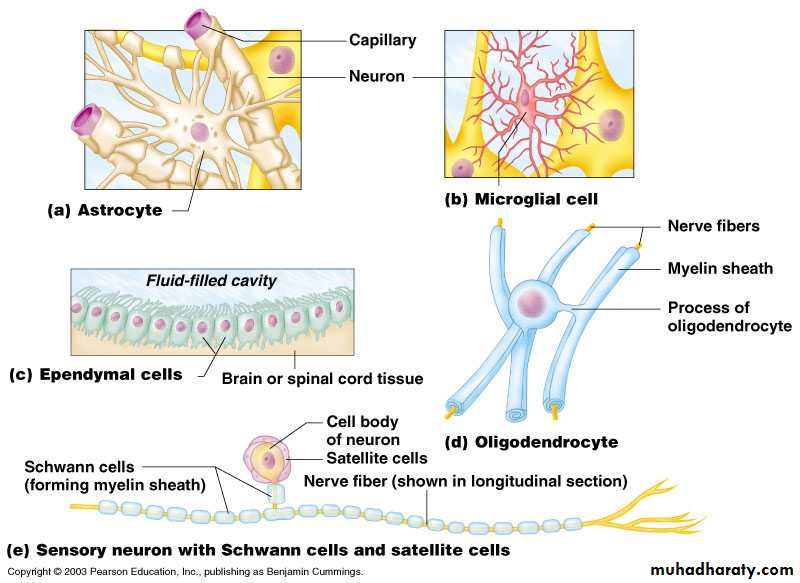
Astrocytes
Form the blood-brain barrier
Form a structural framework for the CNS
Repair damaged neural tissue
Control the interstitial environment of the CNS
Oligodendrocytes Form myelin sheaths CNS
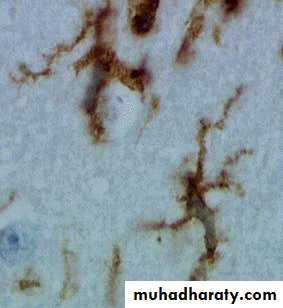
Microglia
Phagocytose foreign microbes, etc.
Ependymal
Line ventricles of the brain, secrete cerebrospinal fluid
Neuroglia of PNS
Schwann cells
Form myelin sheaths of PNS
Satellite cells
Nerve Fibers of the PNS
An axon and its sheaths
Myelinated axon
Axon is surrounded by a myelin sheath
Unmyelinated axon
Axon has no myelin sheath
Structural Classification Neurons
Nervous Tissue: Support Cells (Neuroglia or Glia)
Astrocytes
Abundant, star-shaped cells
Brace neurons
Form barrier between capillaries and neurons
Control the chemical environment of the brain (CNS)
Nutrition.
Microglia (CNS)
Spider-like phagocytes
Dispose of debris
Ependymal cells (CNS)
Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord
Circulate cerebrospinal fluid
Oligodendrocytes(CNS)
Produce myelin sheath around nerve fibers in the central nervous system
Blood Brain Barrier : Function
BrainCapillaryBlood-Brain Barrier TypicalCapillaryMaintains stable brain environment large fluctuations in peripheryBarrier to poisons
Retains neurotransmtters
& other chemicals
Regulates nutrient supplies
glucose levels
active transport ~
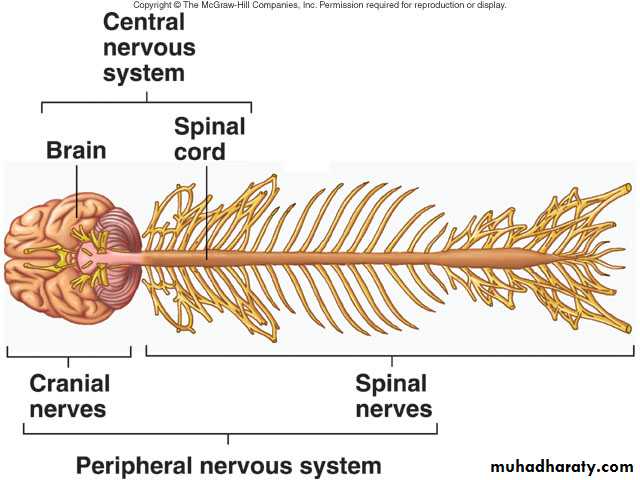
Structural Classification of the Nervous System
Central nervous system (CNS)
Brain
Spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Nerve outside the brain and spinal cord
Central Nervous System:
Consists of Brain Located in cranial vault of skull
And Spinal cord Located in vertebral canal . Brain and spinal cord Continuous with each other at foramen magnum
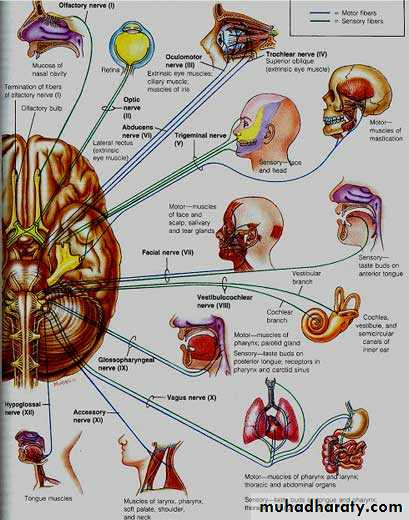
Peripheral Nervous System: comprises peripheral nerves (cranial & spinal ) & ganglia
Two subcategories
Sensory or afferent (input)
Motor or efferent (output)
Divisions
Somatic nervous system
Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Enteric
PNS (Cranial Nerves )
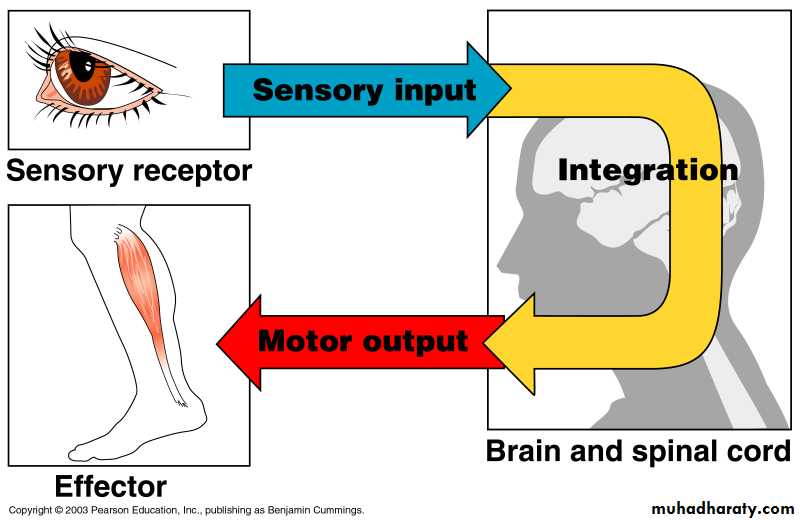
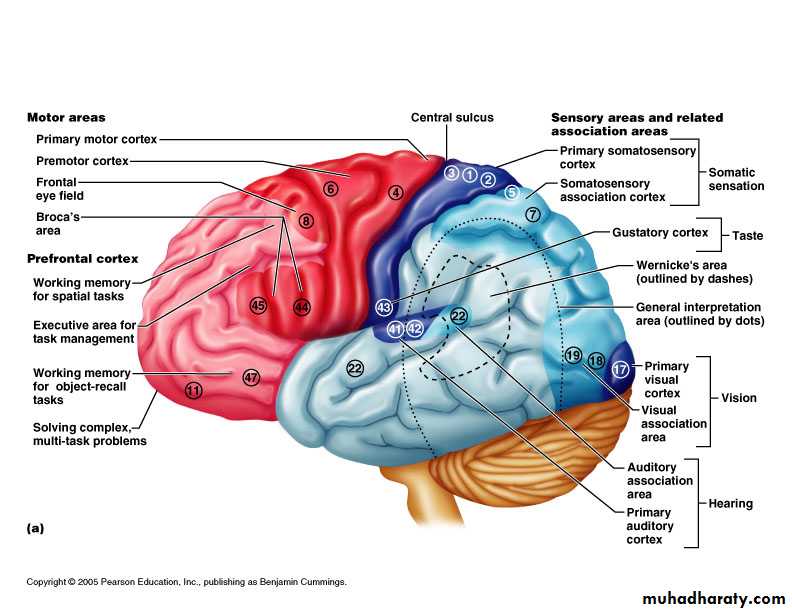
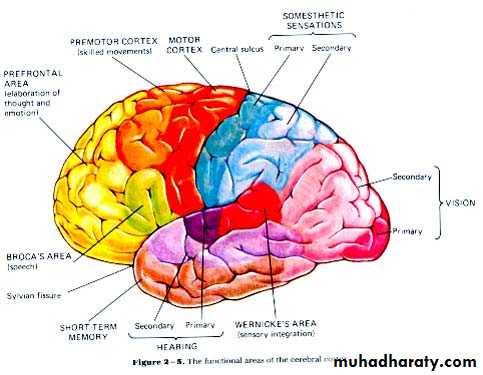
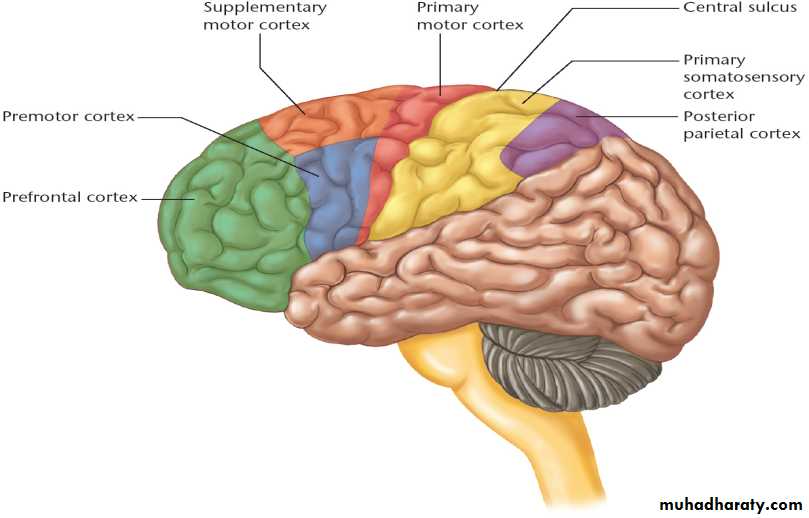
Functions of the Nervous System
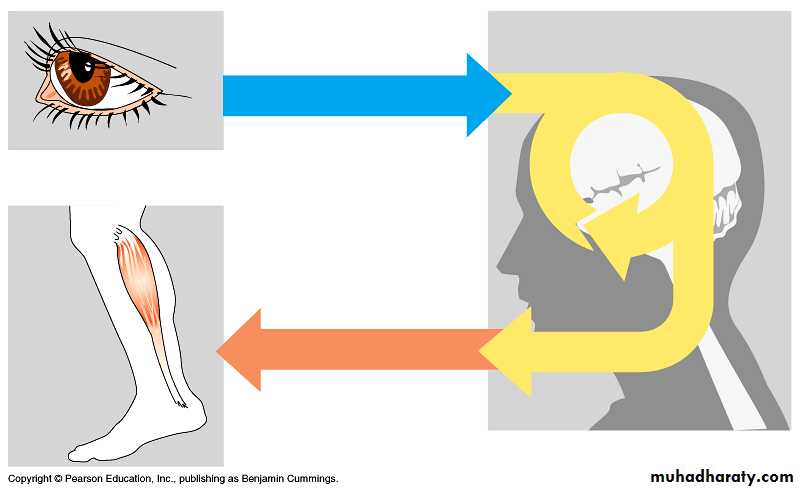
1. Sensory input – gathering informationTo monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli)
2. Integration –
to process and interpret sensory input and decide if action is needed.
3. Motor output
A response to integrated stimuli
The response activates muscles or glands
Functional Classification of the Peripheral Nervous System
Sensory (afferent) division
Nerve fibers that carry information to the central nervous system
Motor (efferent) division
Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system
Motor (efferent) division
Two subdivisions
Somatic nervous system = voluntary
Autonomic nervous system = involuntary
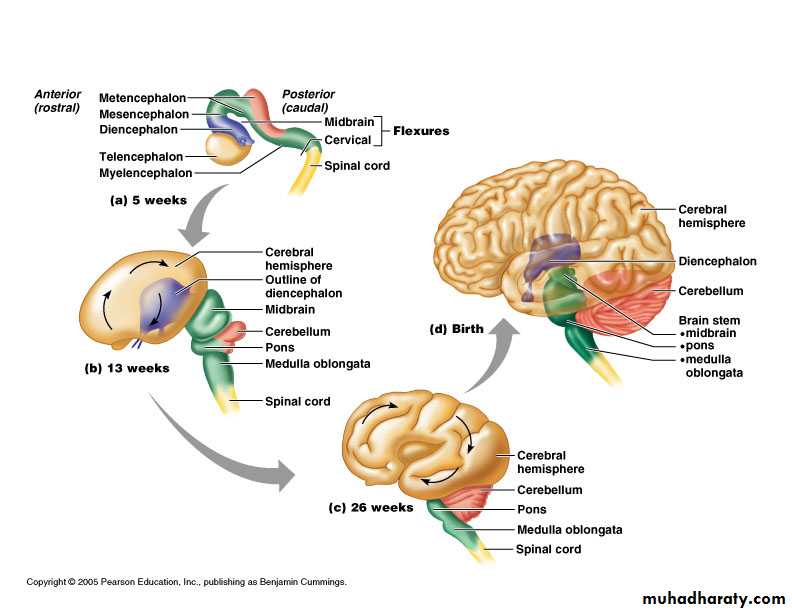
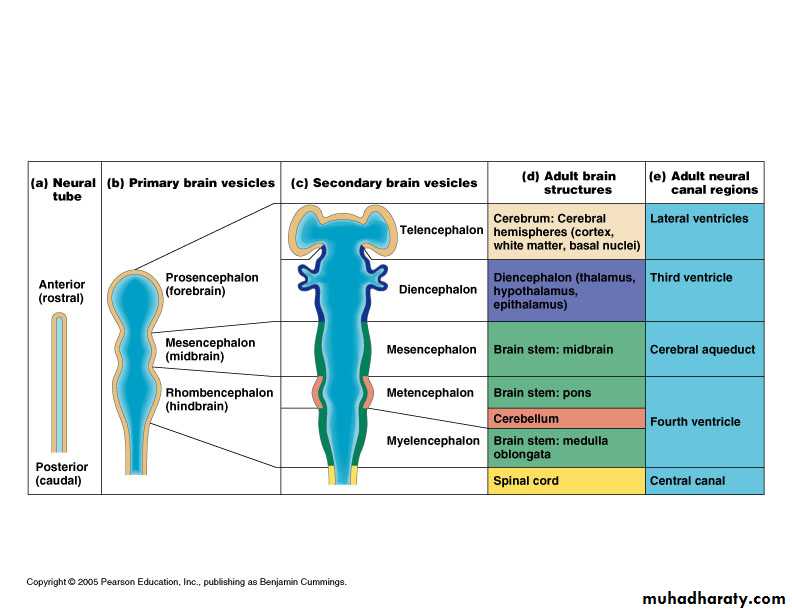
Anatomical classification
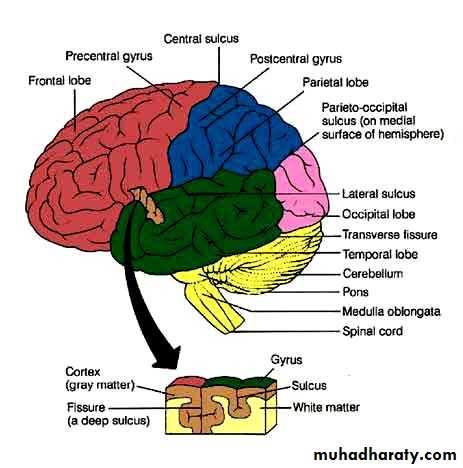
Cerebral hemispheres
Diencephalon
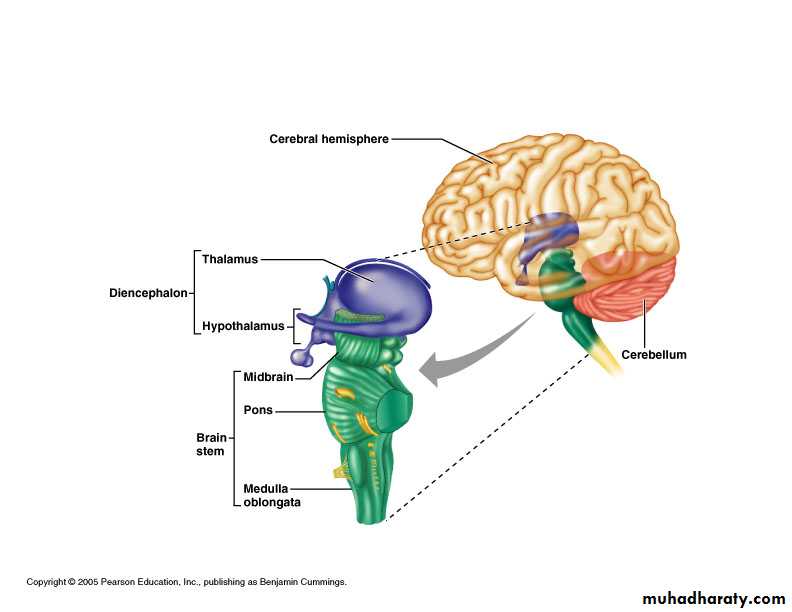
Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Brain stem
Midbrain
Pons
Medulla
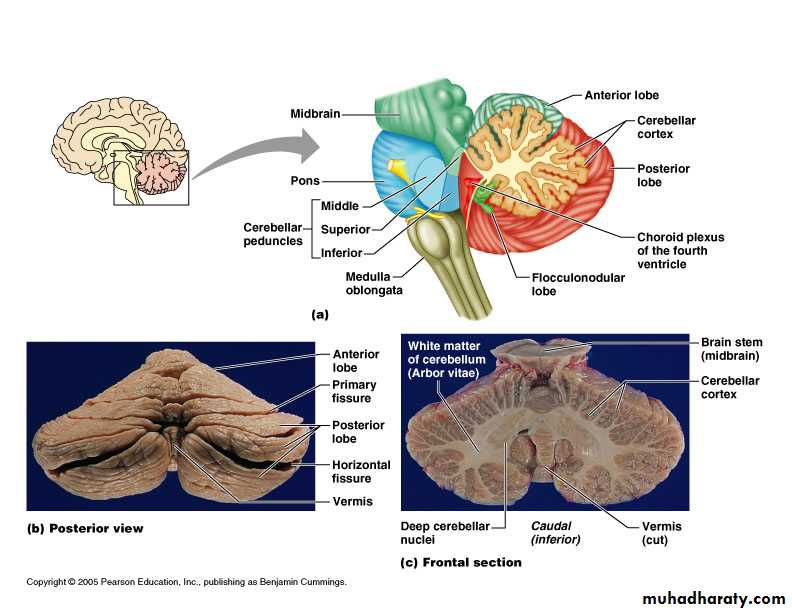
Cerebellum
Spinal cord
Parts of Brain
Cerebrum
Diencephalon
Brainstem
Cerebellum
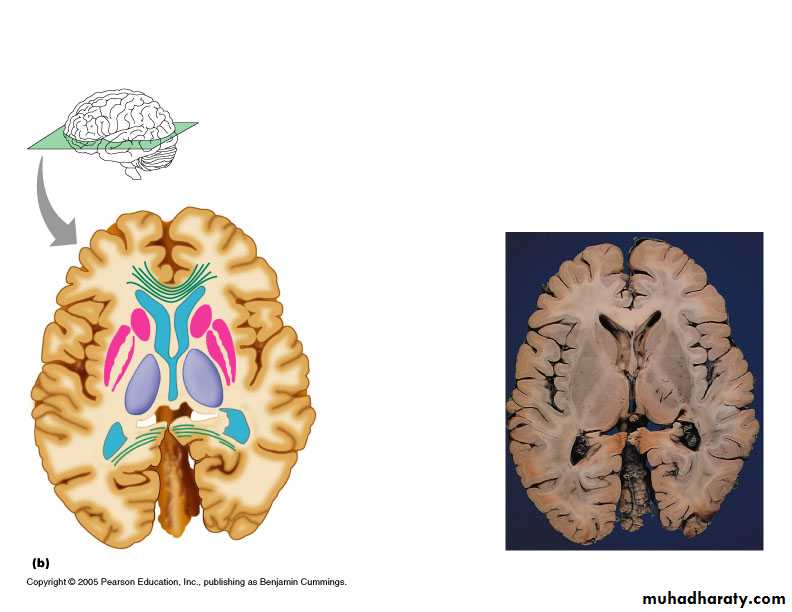
Usual pattern of gray/white in CNS
White exterior to gray
Gray surrounds hollow central cavity
Two regions with additional gray called “cortex”
Cerebrum: “cerebral cortex”
Cerebellum: “cerebellar cortex”
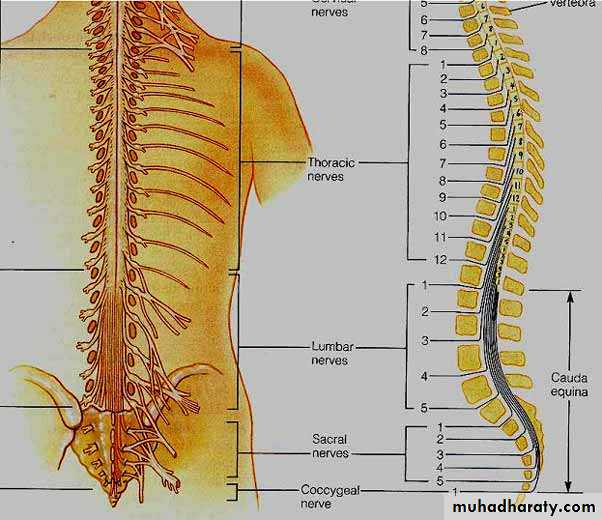
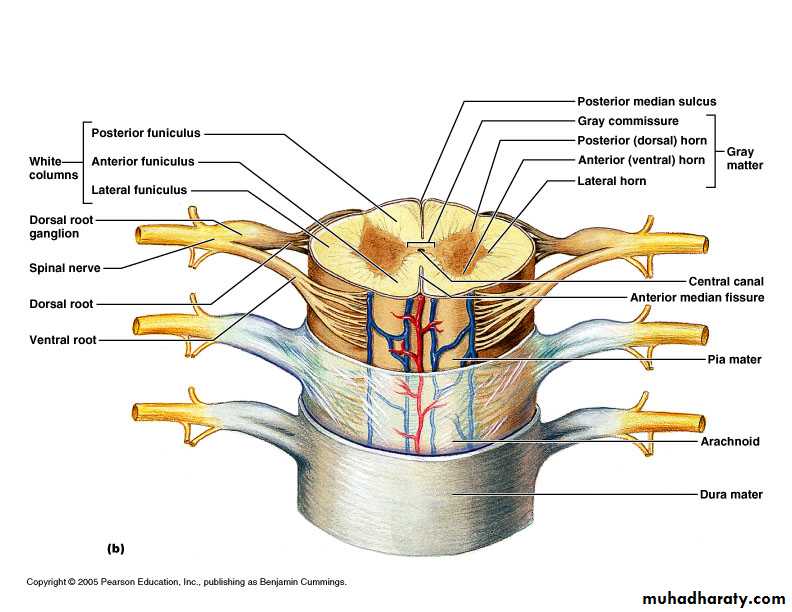
Spinal cord anatomy
Gray commissure with central canalColumns of gray running the length of the spinal cord
Posterior (dorsal) horns (cell bodies of interneurons)
Anterior (ventral) horns (cell bodies of motor neurons)
Lateral horns in thoracic and superior lumbar cord
White matter of the spinal cord (myelinated and unmyelinated axons)
Ascending fibers: sensory information from sensory neurons of body up to brain
Descending fibers: motor instructions from brain to spinal cord
Stimulates contraction of body’s muscles
Stimumulates secretion from body’s glands
Commissural fibers: white-matter fibers crossing from one side of cord to the other
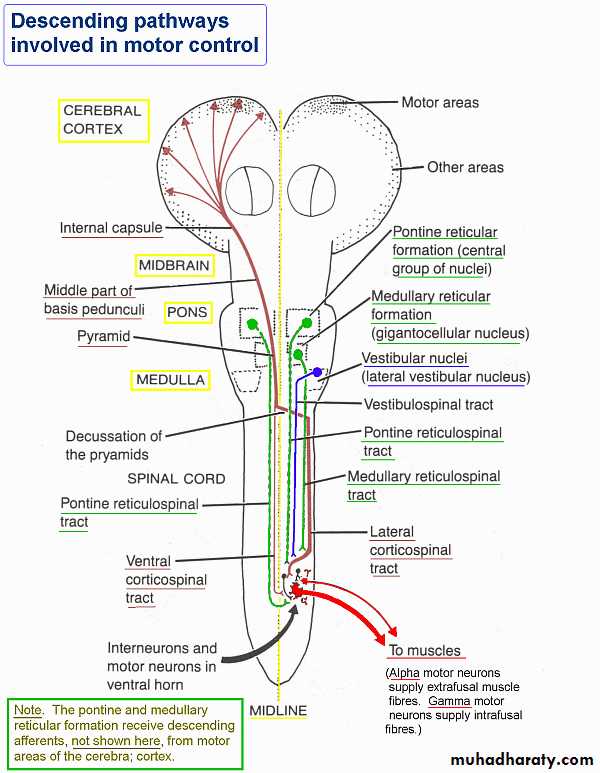
Most pathways cross (or decussate) at some point
Most synapse two or three times along the way, e.g. in brain stem, thalamus or other
Anatomical Tracts
1- Motor system2- Somatic –sensory system
Types Of Lesions
UMNLPower: decreaseTone spastic Reflexes increasesMuscle wasting no Planter reflex upwardAbdominal reflex absent
LMNL decreaseflacciddecreasesyesDownwardpresent
younis alomary