Thoracic Surgery
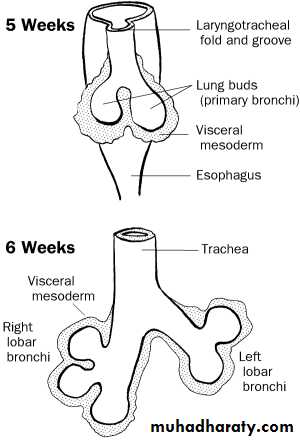
Introduction toEmbryology:
Anatomy:
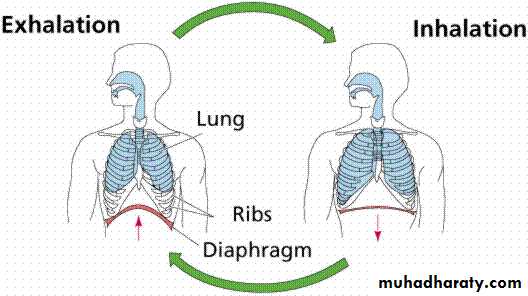
Mechanism of breathing
• Spirometry
• ppo FEV1• DLCO
• VO2 max
• V/P scan
Bronchoscopy:
• Hemoptysis
• Chronic cough
• Localized wheeze
• Pulmonary mass on chest X-ray
• Recurrent or unresolved pneumonia
• Preoperative resectability assessment
• Suspicion of malignancy;
• Indications:
Indications (cont.):
Therapeutic:• Foreign body inhalation
• Difficult intubation
• Atelectasis
• Stricture dilatation
• Lung abscess drainage
• Laser therapy
• Cryotherapy
• Brachytherapy
Flexible Bronchoscopes:
• Better patient tolerance
• Topical anesthesia
• Wider field of view
• Flexibility
• Ambulatory setting
• Useful in patients with cervical spine disorders.
• Allows assessing movement of vocal cords.
• Advantages:
Disadvantages:
• Small instrument channel size• Difficulties in sterilization and maintenance
• Impinges on the airway
• Needs patient cooperation
•
Rigid Bronchocopes:
• Durability
• Large instrument channels
• Control of airway
• Advantages:
Disadvantages:
• Needs general anesthesia• Limited distal visualization
• Higher cost
• Higher risk of trauma
• Contraindications:
• Thoracic aortic aneurysm
• Cervical spine disorders
Complication of bronchoscopy
• Laryngospasm and / or bronchospasm• Hypoxemia
• Tracheal or bronchial obstruction
• Tracheal or bronchial perforation
• Bleeding
• Arrhythmias and cardiac arrest
• Pneumonia
• Air embolism
• Pneumothorax
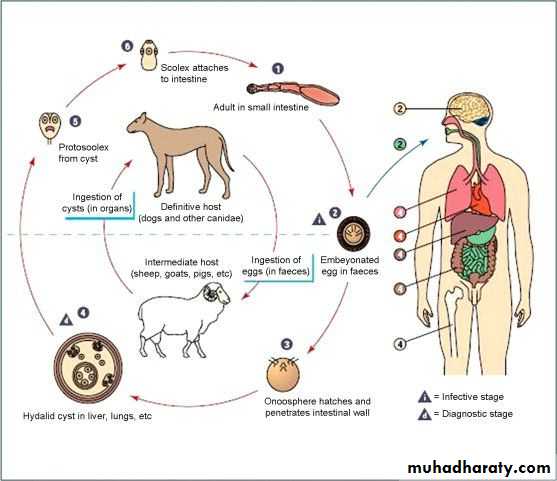
Pulmonary Hydatid Disease:
Cyst full of water
Echinococcus granulosus
Pathology:
• Adventicia
• (host tissue)• Ectocyst
• (Laminated membrane)
• Endocyst
• (germinal layer)
• Broad capsule
Clinical presentation:
• Asymptomatic• Rupture →cough, hemoptysis, watery sputum
• Coughing up "grape skin"
• 2ry infection →fever, rigor, purulent sputum
• Hydropneumothorax or pyopneumothorax
• Anaphylaxis
Investigations:
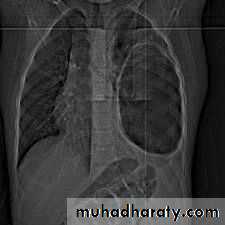
1. CXR 2. CT scan
1) well defined circular or oval homogenous opacity
2) perivesicular pneumocyst or signet ring sign
3) An empty cavity
4) Bilateral and multiple cysts
5) Hydro- or pyo-pneumothorax
Treatment:
Surgical treatment:• Removal of the cyst
• Aspiration / evacuation technique
• Enucleation technique
• Excision
• Anatomical resection:
• Segmentectomy
• Lobectomy
• Pneumonectomy
Medical treatment:
• not effective
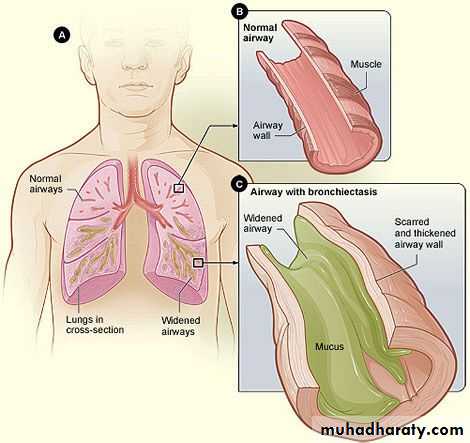
Bronchiectasis:
Causes:• Congenital
• Acquired•
Clinical presentaion:
• A persistent productive cough of purulent sputum, with fetor oris.• Hemoptysis
• Recurrent pneumonitis
• On examination:
• Cyanosis,
• Clubbing
• Coarse crepitations.
Investigations:
• CXR• CT scan
• Bronchography
Treatment:
Medical treatment:• Prevent infection
• Physiotherapy and postural drainage
Surgical treatment indicated in:
• Localized bronchiectasis• Massive hemoptysis
• Recurrent suppurition
• Anatomical resection
Lung Abscess:
• Primary necrotizing pneumonia• Aspiration pneumonia
• Bronchial obstruction
• Systemic sepsis
• Pulmonary trauma
• Direct extension
• Causes:
Diagnosis:
Fever, poor appetite, malaise, dyspnea, copious purulent sputum, hemoptysis
CXR
CT scan
Sputum culture
Bronchoscope
Treatment:
Medical treatment:Prolonged antimicrobial therapy
Drainage
Surgical treatment:
No responseSuspicion of malignancy
Significant hemoptysis
Complications of lung abscess